FIGURE 3.
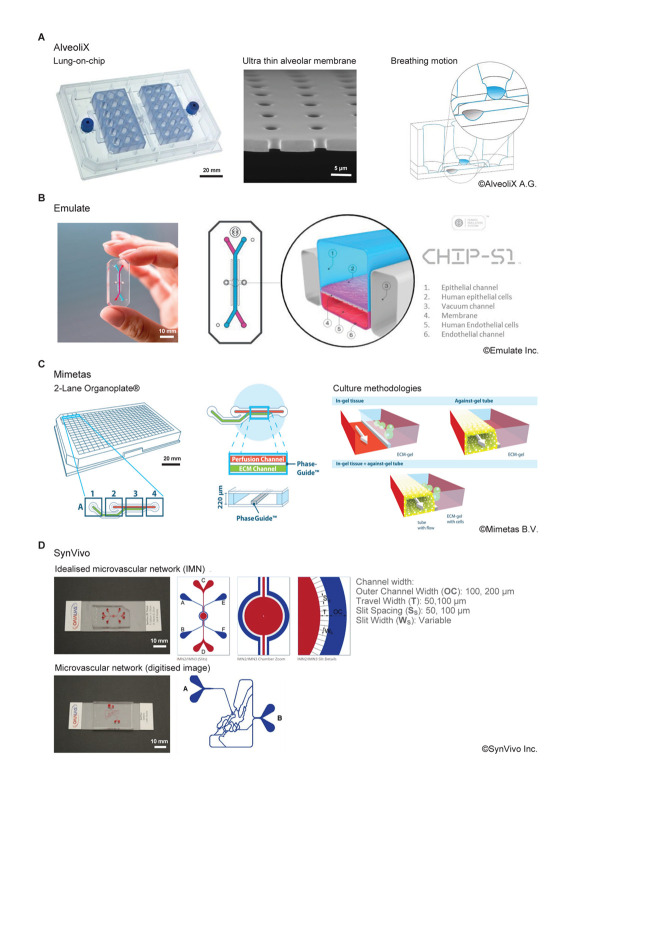
Comparison of commercially available organ-on-chip platforms incorporating a form of active biophysical stimulus. (A) AX12 lung chip based on a 96-well plate format, consisting of two chips supported by a plate, each of which comprise six independent units. The ultrathin membrane (blue) is deflected by negative pressure inside the basal chip chamber through an integrated micro-diaphragm (gray). Images© Alveolix A.G. (B) The Human Emulation system from Emulate Inc. comprising organ chips which fit into the PodTM carrier. The ZoëTM culture module controls the rate of flow and stretch for up to 12 chips. The OrbTM provides the precise mixture of gas, power, and vacuum stretch required by the ZoëTM culture module. Images© Emulate Inc. (C) The 2-lane OrganoplateTM from Mimetas. Based on a 384-well plate format, it can support 96-individual models. Cells are cultured in/on ECM alongside a perfusion channel created using unique phase guide technology. Images© Mimetas B.V. (D) SynVivo’s microfluidic chips create an idealized microvascular network to mimic the formation of, and transport across, tight and gap junctions. Networks can also be created from digitized images to replicate in vivo physiology more accurately. Natural tissue regions can also be incorporated within the network topology. Images© SynVivo Inc.