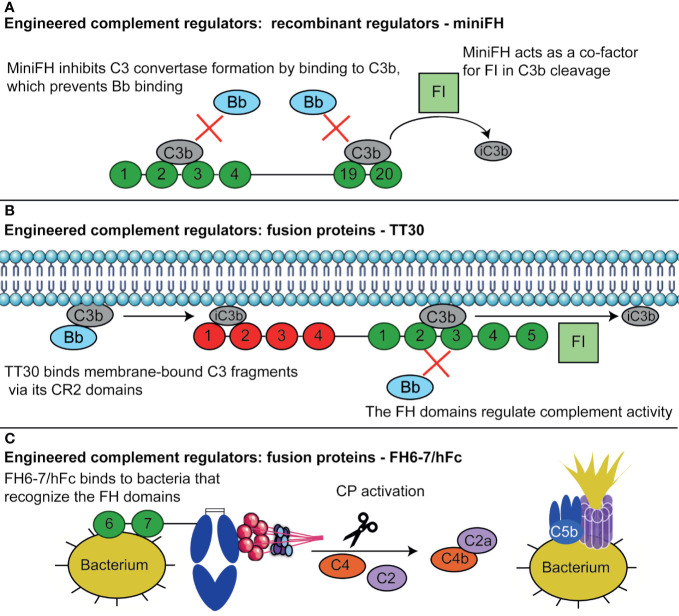
Figure 3.
Therapeutics based of complement regulators. (A) MiniFH has been designed from FH CCPs 1-4 and 19-20 to open up an extra C3b binding domain. This means it can bind two C3b molecules simultaneously, where regular FH can only bind one. MiniFH inhibits C3bBb formation and exert FI co-factor activity. (B) TT30 is a fusion protein of the first 4 domains of CR2 and the first 5 domains of FH. The CR2 domains recognize tissue-bound C3 fragments, while the FH domains regulate complement activity. Thus, the protein is targeted towards tissues where complement is already activated, where the FH domains can then exert complement regulatory activity. (C) FH6-7/hFc contains FH CCP 6 and 7, and the Fc part of an antibody. Certain bacteria bind FH via CCP FH6-7, normally to evade the complement system. These CCPs are utilized here to target these bacteria, upon which the hFc induces CP activation by C1q binding resulting in complement activation via the CP finally resulting in opsonization and lysis of bacteria. Figure designed using Servier Medical Art.