Figure 1.
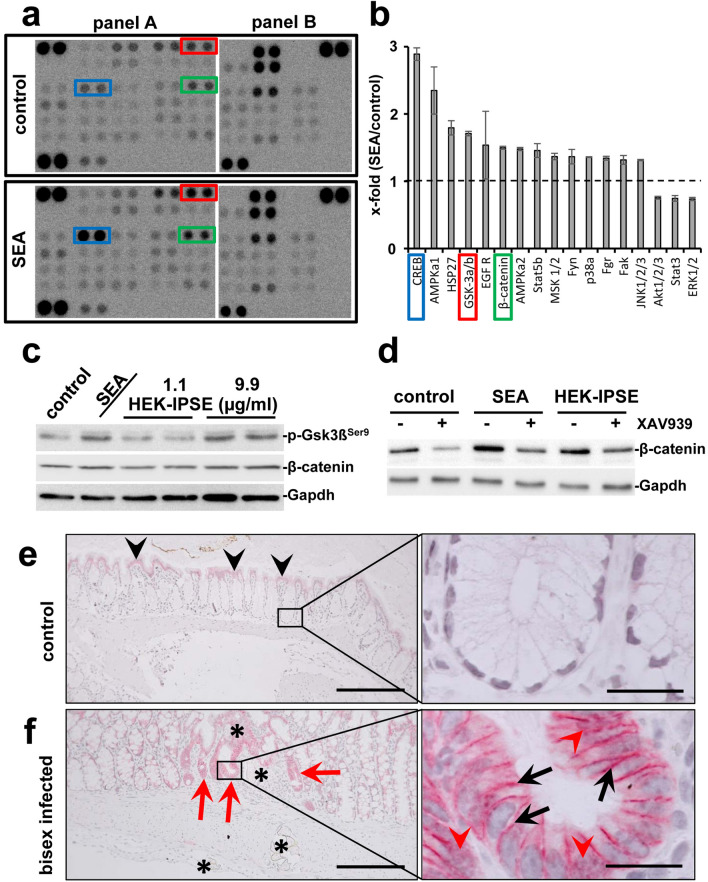
Eggs of S. mansoni induce Wnt-signaling/ß-Catenin in colon epithelium. (a) Phosphokinase proteome profiler arrays and (b) densitometric assessment thereof demonstrated the induction of β-catenin as well as the phosphorylation of Gsk3β and CREB in SW620 cells after soluble egg antigen (SEA)-stimulation. The 17 most regulated factors of the array are depicted in (b). The Human Phospho-Kinase Array is a tool to simultaneously detect the relative levels of phosphorylation of kinases and two related total proteins. The array consists of two membranes (left and right membrane of each panel) on which each kinase or substrate was analyzed in duplicates. The experiment and assay was performed twice. The positions of β-catenin (green box), pGsk3β (red box), and CREB (blue box) are highlighted. (c) Western blot analysis showed the phosphorylation of Gsk3β and indicated a slightly enhanced β-catenin expression in SW620 cells stimulated with SEA and HEK-IPSE for 4 h. Gapdh was used as loading control. The experiment and assay were reproduced at least two times. Representative blots are shown. The quantification is presented in Suppl. Fig. 1. (d) Inhibition of Wnt-signaling by the tankyrase inhibitor XAV939 demonstrated a reduction of SEA-induced β-catenin. The experiment and assay were reproduced at least two times. The cells were pretreated with XAV939 for 15 h and during the 4-h-stimulation. Representative blots are shown. The quantification is presented in Suppl. Fig. 2. (e) Immunostaining of β-catenin in the colon of control hamsters visualized low amounts of epithelial β-catenin at the luminal side of the colon (black arrowheads), but not in those enterocytes inside the crypts (magnification of the boxed area is depicted in the right panel). (f) Enhanced expression of β-catenin was observed at the bottom of those crypts around the extravasation sites of S. mansoni eggs in bisex-infected hamster colon (red arrows). Please note that enhanced nuclear translocation of β-catenin in enterocytes at the bottom of those crypts, which surround the extravasation sites of S. mansoni eggs in bisex-infected hamster colon (red arrowheads in the magnified area, right panel). The black arrows depict enhanced intercellular accumulation of β-catenin. S. mansoni eggs (*), magnification 200×, bar 200 µm (left panels) and 1000×, bar 20 µm (right panels). The quantification is presented in Suppl. Fig. 3.