FIG. 2.
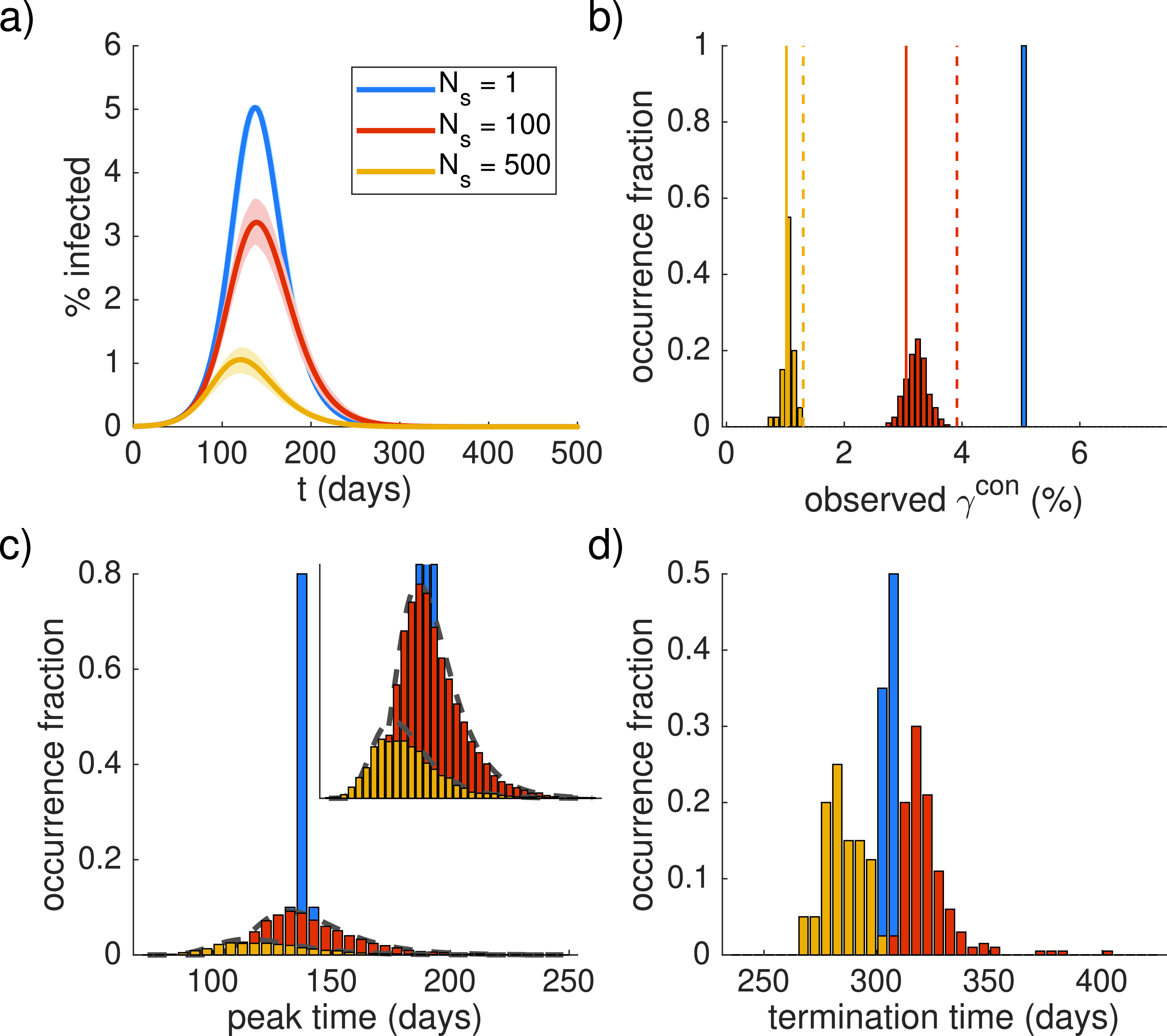
Epidemics for different subdivisions of the population. , , , three different values of , 200, and 40 individual simulations for , , and , respectively. (a) Time courses (solid lines) and 2.5/97.5 percentiles (shading). (b) Distributions of the observed peak percentage (in the whole population). The occurrence fraction indicates the fraction of simulations. Analytical estimates for (dashed lines), Eq. (6), and (solid lines), Eq. (9), assume according to a binomial distribution. (c) Distribution of peak times in the sub-populations. The inset provides an enlarged y-axis. Dashed lines indicate analytical approximation, Eq. (8), assuming a uniform for each case. (d) Distribution of termination times, defined as the time when in the total population drops below .
