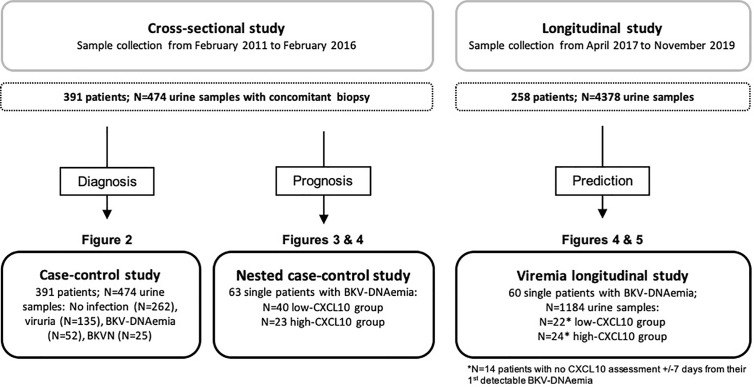
Figure 1.
Design of the cross-sectional and longitudinal studies. In the cross-sectional study, all data and samples were collected at a single time point: an allograft biopsy was performed at the time (±7 days) of BKV viral load assessment. The different stages of BKV reactivation were defined as follows: the no BKV infection group, viruria group (viruria was detected in the absence of BKV-DNAemia and BKVN), DNAemia group (positive for BKV-DNAemia, regardless of BKV viruria, with no biopsy-proven BKVN), and BKVN group (positive SV40 staining and/or viral inclusion on the biopsy specimen). Among these 474 samples, BKV-DNAemia was found in N = 52 samples from the DNAemia group and N = 24 samples from the BKVN group. From these 76 samples, we retained the first sample of each patient (N = 63) to participate in the nested case-control study. In the longitudinal study, serial assessment of uCXCL10/cr was performed at predefined time points in all patients consecutively transplanted at Necker Hospital between April 2017 and November 2018. Of these 258 patients, 60 single patients experienced BKV-DNAemia and provided 1,184 samples for uCXCL10/cr quantification. In both BKV-DNAemia cohorts, the patients were divided into 2 groups according to the uCXCL10/cr threshold: the low-CXCL10 group was defined by uCXCL10/cr ≤12.86 ng/mmol, and the high-CXCL10 group was defined by uCXCL10/cr >12.86 ng/mmol.