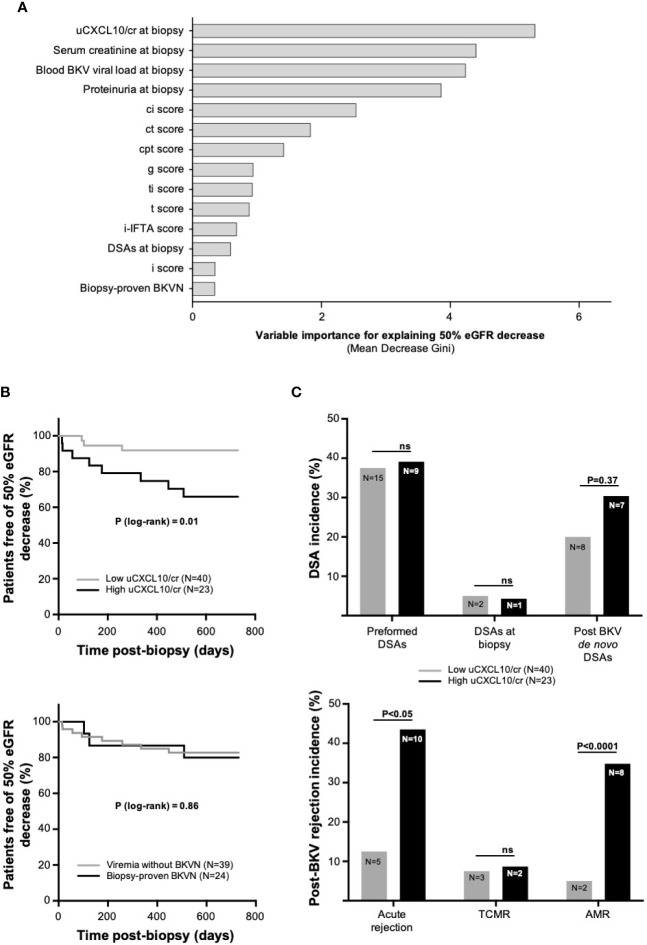
Figure 3.
BKV-DNAemia prognosis analysis (A). Variable importance measures from a random forest analysis. A total of 1,000 classification trees were built to address the endpoint “50% eGFR decrease” in the 63 patients with BKV-DNAemia (nested case-control study). Fourteen variables were included among the biological and histological data. The mean decrease in Gini is the average of a variable’s total decrease in node impurity, weighted by the proportion of samples reaching that node in each individual decision tree. A higher mean decrease in Gini indicates higher variable importance (B). Kaplan-Meier curves illustrating survival before the occurrence of a 50% eGFR decrease in the low- and high-CXCL10 groups (upper panel) and in two groups of viremic patients with or without BKVN (lower panel). The P-value was computed from a log-rank test (C). Histograms comparing DSA incidence in the low- and high-CXCL10 groups (upper panel) at different time points: preformed DSAs, DSAs at the time of biopsy and post-BKV de novo DSAs. The lower panel illustrates the post-BKV occurrence of acute rejection, TCMR and AMR. The P-value was computed from Fisher’s exact test. The low-CXCL10 group was defined by uCXCL10/cr ≤12.86 ng/mmol, and the high-CXCL10 group was defined by uCXCL10/cr >12.86 ng/mmol. AMR, antibody-mediated rejection, BKVN, BKV-associated nephropathy; cr, urinary creatinine; ci, interstitial fibrosis; ct, tubular atrophy; DSAs, donor-specific antibodies; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; g, glomerulitis; i, interstitial infiltrate; i-IFTA, inflammation within areas of interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy; ptc, peritubular capillaritis; t, tubulitis; TCMR, T-cell mediated rejection; ti, total inflammation; ns, not significant.