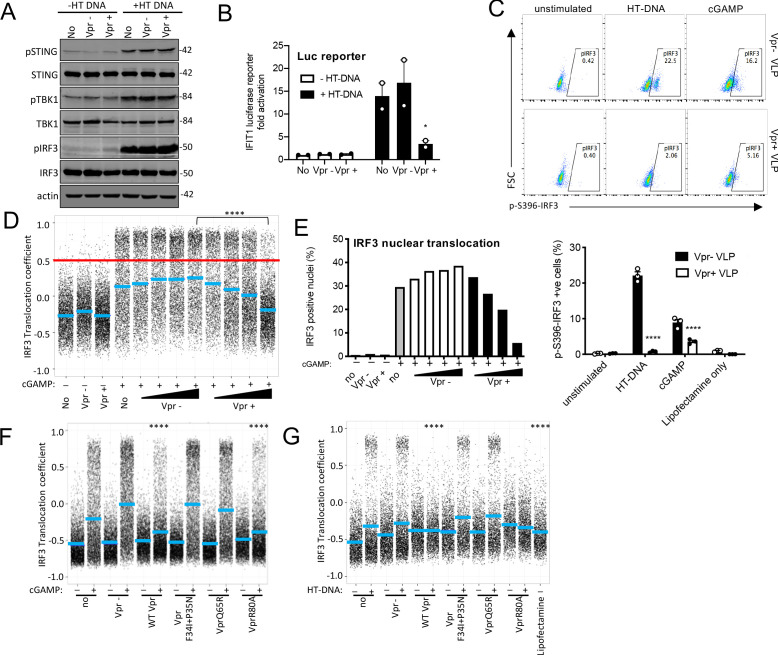
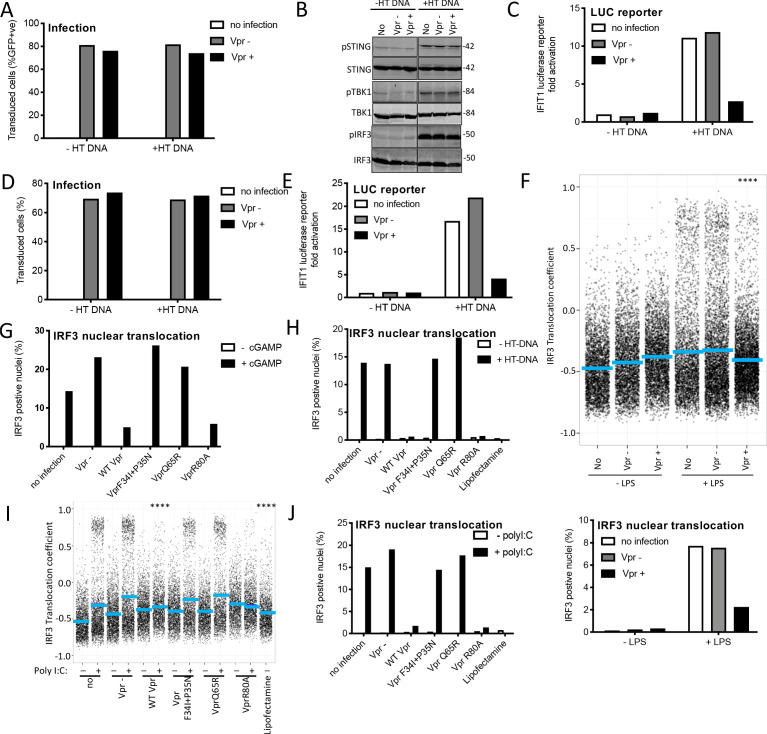
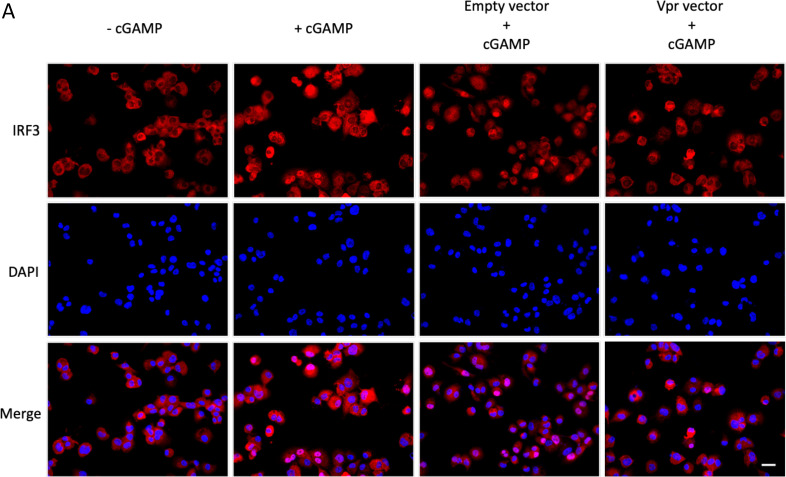
Figure 5. Vpr inhibits IRF3 nuclear translocation.
(A) Immunoblot detecting Phospho-STING (Ser366), total STING, phospho-TBK1 (Ser172), total TBK1, phospho-IRF3 (Ser386), total IRF3, or actin as a loading control, from extracted THP-1 cells expressing Vpr from a lentiviral vector (MOI 1), expressing empty vector, or THP-1 left untransduced as a control and transfected with HT-DNA (5 μg/ml) or left untransfected as a control. Size markers are shown in kDa. (B) Mean fold induction of IFIT1-Luc in cells from A and B (C) Flow cytometry plot (forward scatter vs pIRF3-S396 fluorescence) of THP-1 cells infected with Vpr bearing virus-like particles (VLP) lacking genome (1 RT U/ml), or Vpr free VLP, stimulated with cGAMP (5 μg/ml) or HT-DNA transfection (5 μg/ml). Lower panel shows the flow cytometry data as a bar graph, plotting pIRF3-S396-positive cells. (D) Single-cell immunofluorescence measurement of IRF3 nuclear translocation in PMA differentiated THP-1 cells treated with cGAMP, or left untreated, and infected with HIV-1 GFP bearing Vpr, lacking Vpr or left untransduced. Cells were fixed and stained 3 hrs after infection/transfection. Red line shows the translocation coefficient threshold. Blue lines represent mean translocation coefficient. (E) Percentage of cells in D with IRF3 translocation coefficient greater than 0.5 (above red line). (F) Single-cell immunofluorescence measurement of IRF3 nuclear translocation in PMA-differentiated THP-1 cells stimulated with cGAMP (5 μg/ml), or left unstimulated, and infected with HIV-1 GFP lacking Vpr or bearing WT Vpr or Vpr mutants as shown (1 RT U/ml) or left uninfected. (G) Single cell immunofluorescence measurement of IRF3 nuclear translocation in PMA differentiated THP-1 cells transfected with HT-DNA (5 μg/ml), or left untransfected, and infected with HIV-1 GFP lacking Vpr, or bearing WT or mutant Vpr (1 RT U/ml) or left uninfected. Data in B is expressed as means ± SEM (n = 2). Data is analyzed using two-way ANOVA: * (p<0.05), ** (p<0.01), *** (p<0.001), **** (p<0.0001) compared to data from infection with HIV-1 lacking Vpr. Data are representative of three (C–G) or two (A, B) independent experiments.