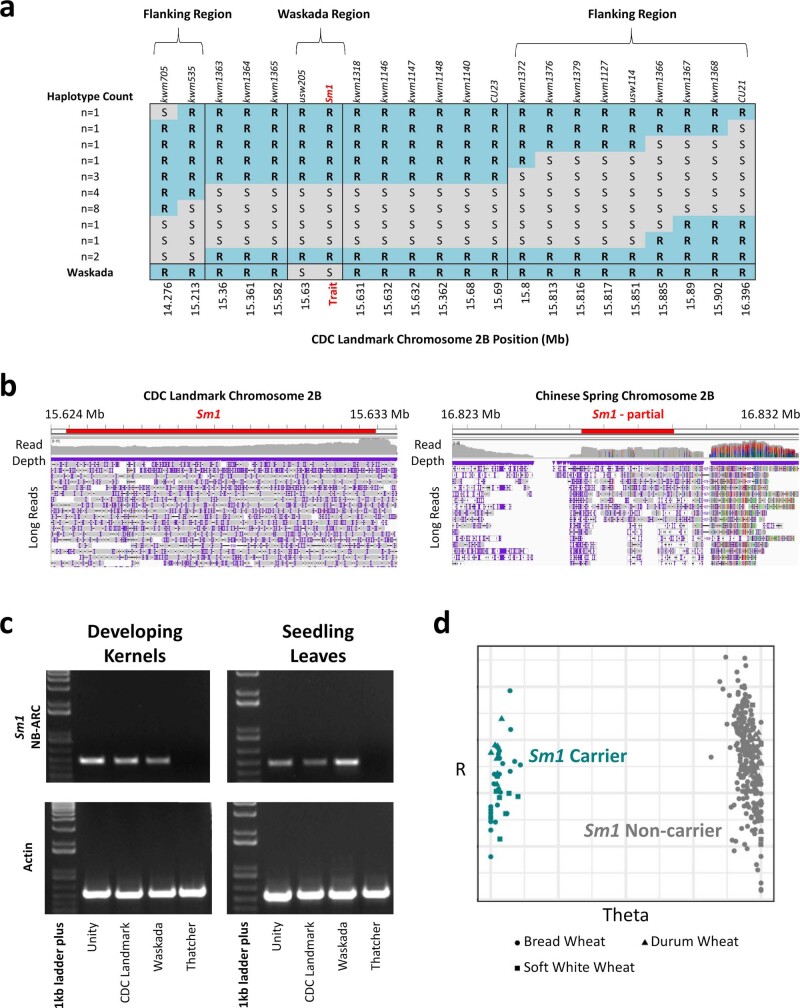
Extended Data Fig. 10. Confirmation of gene expression and gene structure for Sm1.
a, Critical recombinants from the 99B60-EJ2G/Infinity and 99B60-EJ2D/Thatcher populations used to fine map Sm1. The 99B60-EJ2G/Infinity cross had 5,170 F2 plants, while 99B60-EJ2D/Thatcher cross had 5,264 F2 plants; only recombinant haplotypes between orange wheat blossom midge resistant (R) and susceptible (S) genotypes are shown. b, Oxford Nanopore long read confirmation of the Sm1 gene candidate in the CDC Landmark RQA (left), and alternative haplotype in Chinese Spring (right). Vertical coloured lines indicate sequence variants. c, Amplification of cDNA for the NB-ARC domain of the Sm1 gene candidate (top) and actin control (bottom) derived from RNA isolated from developing kernels (left) and wheat seedlings (right). Unity and CDC Landmark are carriers of Sm1. Waskada carries an alternative haplotype and does not carry Sm1 (see main text). Thatcher was used as a susceptible parent for fine mapping of Sm1 and does not contain the associated NB-ARC domain. The experiment was replicated on four independent biological samples for each condition. d, Distribution of an Sm1 allele-specific PCR marker in a diverse panel of >300 wheat lines.