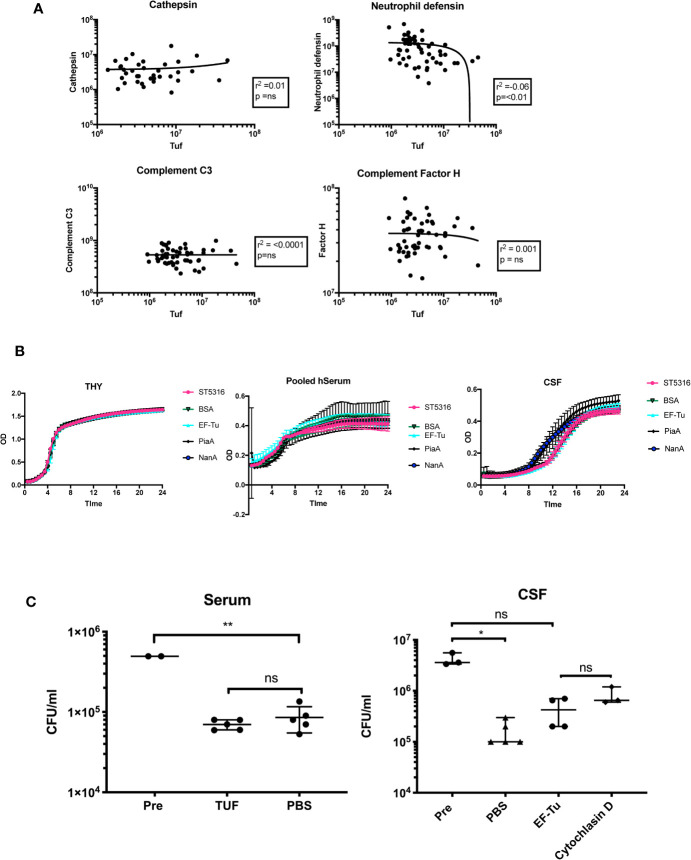
Figure 4.
EF-Tu negatively correlates with neutrophil defensin in CSF, and effects on neutrophil-mediated killing in CSF but not serum. (A) EF-TU negatively correlates with neutrophil defensin. Estimates of the abundance of Tuf (x axis, log10 scale) plotted against abundance of highly expressed proteins (y axis, log10 scale) known to interact with S. pneumoniae (complement C3, Factor H), and the most highly abundant neutrophil protein, Neutrophil defensin (A). Correlation estimated with Spearman’s test. (B) EF-Tu does not enhance ST5316 growth in CSF, serum or THY. Growth curves of S. pneumoniae serotype 1 strain ST5316 in Todd-Hewitt broth supplemented with 0.5% yeast extract (THY), pooled human serum and human CSF. Growth plotted over time (x axis) against optical density (y axis) at 620 nm. Growth in normal CSF compared to growth supplemented with 40 ug of recombinant EF-Tu. Additional proteins used as controls, bovine serum albumin (BSA), neuroaminidase A (NanA), and pneumococcal iron acquisition system A (PiaA). (C) EF-Tu effects on neutrophil mediated killing of S. pneumoniae in CSF but not serum. Viable S. pneumoniae strain ST5316 after 45 min neutrophil opsonophagocytosis assay, supplemented with 400 ug of recombinant Tuf protein. Bacteria opsonized with serum (left panel) and CSF (right panel). Viability measured by colony forming unit (CFU) counts on blood agar after 18 h incubation. Data expressed as medians with range. Statistical significance calculated using the Mann-Whitney U test.