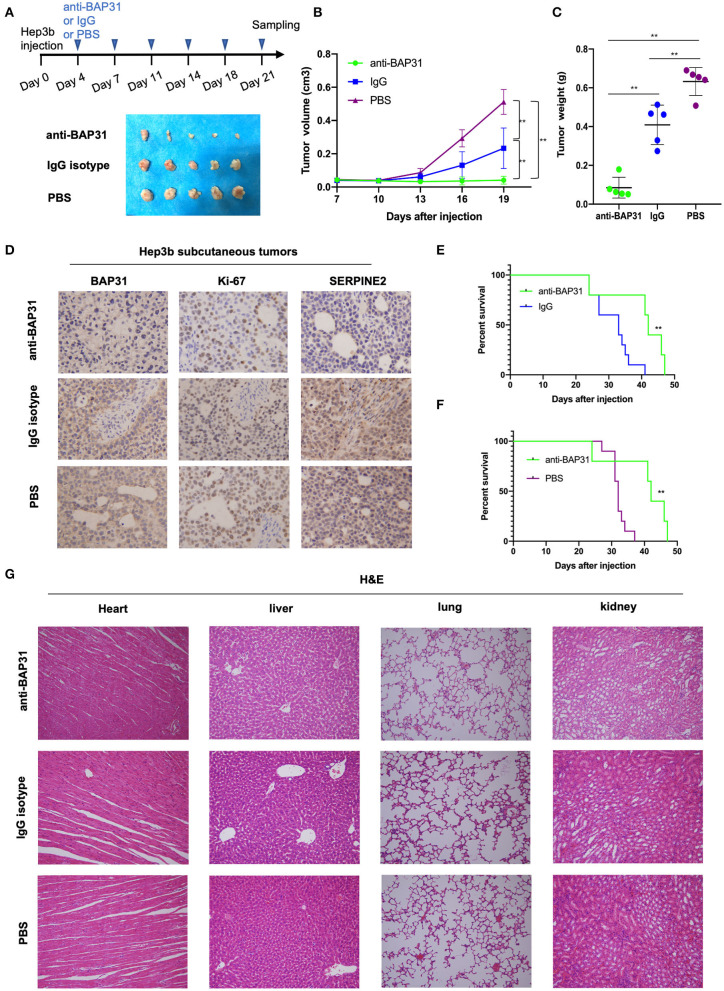
Figure 6.
Anti-BAP31 antibody inhibits HCC cell-induced tumor formation. (A) Hep3b cells were injected subcutaneously into the right flank of nude mice on day 0. Starting from day 4, anti-BAP31 antibody, mouse IgG isotype, and PBS were administered intraperitoneally twice a week. Images of the xenograft tumors are shown. (B) Growth curve of xenografts of Hep3b cells treated with anti-BAP31, mouse IgG isotype, and PBS (n = 5, mean ± SD). (C) Weight of the xenograft tumors was measured. The results represent the mean ± SD, and **p < 0.01 was considered to be significant according to Student's t-test. (D) Expression levels of BAP31, Ki-67, and SERPINE2 in Hep3b subcutaneous tumors were monitored by IHC analysis. (E,F) Kaplan–Meier survival curve representing the overall survival of mice injected with Hep3b cells and treated with anti-BAP31 antibody, mouse IgG isotype, and PBS (n = 10, **p < 0.01 by log-rank test). (G) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the heart, liver, lung, and kidney in various groups of mice. BAP31, B-cell receptor-associated protein 31; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; IHC, immunohistochemistry; SERPINE2, serpin family E member 2; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.