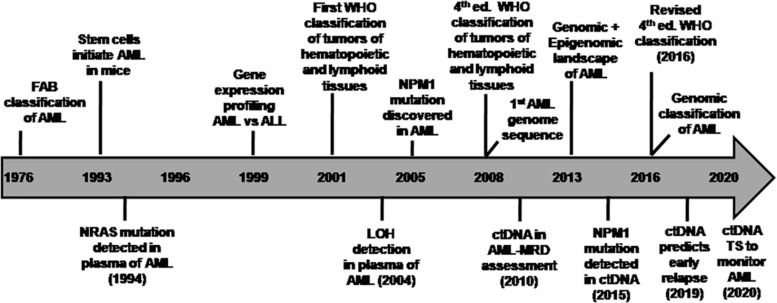
FIGURE 1.
Timeline of various milestones in the evolution of genomic classification of AML (Adapted from TCGA project Ley et al., 2013) and studies on circulating tumor DNA in AML. Initially, AML was classified by the French-American-British (FAB) Cooperative Group (1976) based on the cell lineage of leukemic cells and their differentiation status derived from the cell morphology as well as cytochemical staining of BM cells (Bennett et al., 1976). This approach had limitations in risk stratification in majority of AML cases. The discovery of recurrent cytogenetic abnormalities led to a novel classification system by the World Health Organization [WHO] (2001), which was revised in 2008 and later in the 2016 WHO Classification. Few research highlights of various studies on ctDNA analysis in AML disease monitoring are indicated in the timeline as a co-evolution with advances in AML genomics. ALL, acute lymphoblastic leukemia; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; ctDNA, circulating tumor-derived DNA; ed., edition; LOH, loss of helerozygosity; MRD, measurable residual disease; TS, targeted sequencing; WHO, World Health Organization.