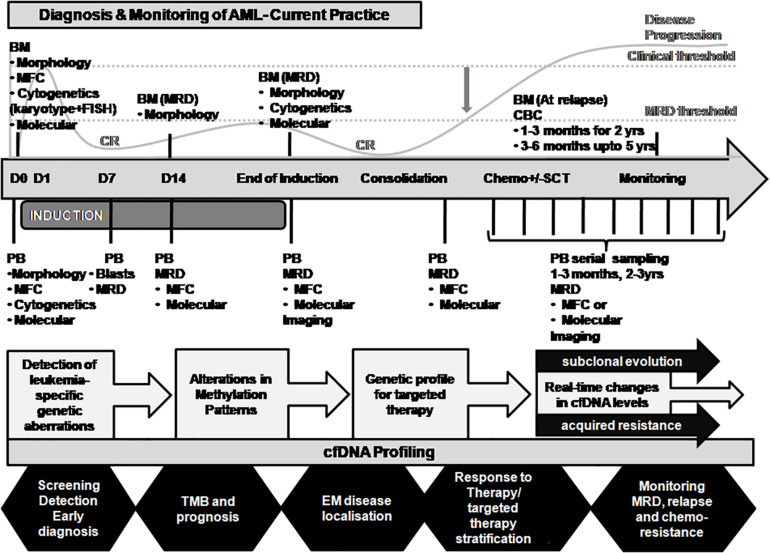
FIGURE 4.
Proposed integration of ctDNA profiling with AML diagnosis and disease monitoring. The current practice for AML diagnosis and disease monitoring is primarily dependent on the bone marrow sampling. A representation of the disease course is merged with the major time-points of investigation for evaluation of response to treatment (top panel). A critical time point post-chemotherapy needs to be defined when the disease is in occult stage and the MRD threshold is maintained (indicated by the gray downward arrow). Residual AML disease monitoring by serial sampling of circulating cfDNA analysis for patient-specific genetic alterations may prove informative when MRD threshold is breached (indicated in the middle panel). cfDNA profiling may provide several other applications in AML disease monitoring in real time as shown (bottom panel). BM, bone marrow; CBC, complete blood count; cfDNA, cell-free DNA; CR, clinical remission; MFC, multiparametric flow cytometry; MRD, measurable residual disease; PB, peripheral blood; SCT, stem cell transplantation; TMB, tumor mutation burden.