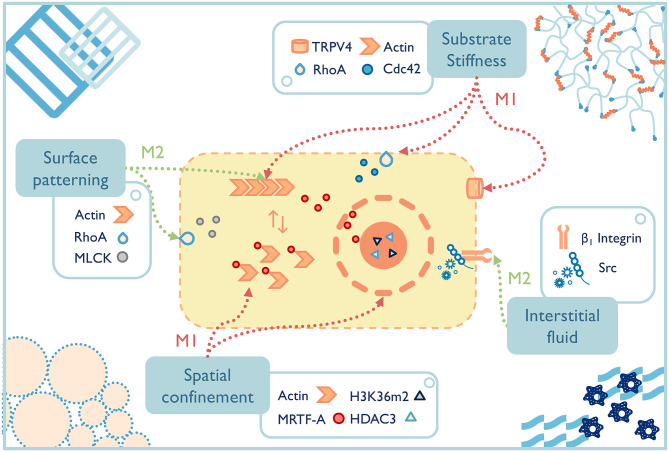
Figure 4.
The fate of macrophages can be greatly affected by material properties, both those inherent to the selected materials and the additional engineered functionality. Potential macrophage mechanotransduction pathways have been probed for a few properties, such as surface patterning (McWhorter et al., 2013), substrate stiffness (Patel et al., 2012; Scheraga et al., 2016; Gruber et al., 2018), spatial confinement (Jain and Vogel, 2018), and interstitial fluid (Li R. et al., 2018), while others remain to be elucidated. TRPV4, transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 4; RhoA, ras homolog family member A; Cdc 42, cell division cycle 42; MLCK, myosin light-chain kinase; HDAC, histone deacetylase 3; MRTF-A, myocardin-related transcription factor-A.