FIGURE 1.
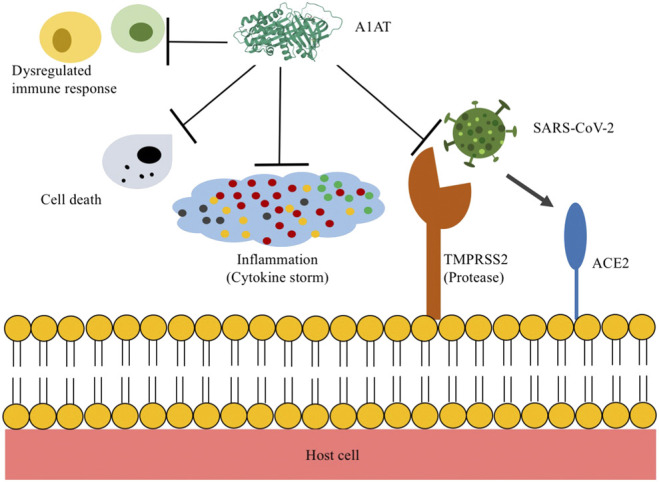
Proposed mechanisms of alpha-1 antitrypsin (A1AT) in COVID-19 treatment. The entry of SARS-CoV2 into host cells is through the binding of viral S-protein to angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) located on host cells, which is mediated by the transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2). A1AT inhibits TMPRSS2, thus, reduces SARS-CoV-2 infection. In addition, A1AT can reduce acute inflammatory responses, cell death, neutrophil elastase trap formation, coagulative activity, and dysregulated immune responses.
