| IFN production |
Produced downstream TLR3, TLR4 (endosomes), RLRs, STING (32–35) Produced by MAVS located on mitochondria (38, 39)
|
Produced downstream TLR3, TLR4 (endosomes), RLRs, STING (32–35) Produced by MAVS located on both mitochondria and peroxisomes (38, 39)
|
| Receptor distribution |
|
|
| JAK/STAT signaling |
Requires JAK1 (JAK2 independent) (30, 39, 55, 57–59, 64, 72) Signaling is TYK2 dependent (52–55)
|
Requires JAK1 and JAK2 (30, 39, 72) Signaling is TYK2 independent (61–63)
|
| Other pathways |
|
|
| Magnitude and kinetics of ISG induction |
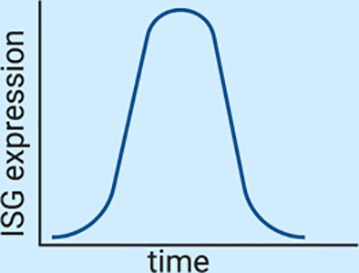
High magnitude of ISG induction (46–48, 83, 85) Fast induction and fast decrease in ISG expression (46–48, 83, 85)
|
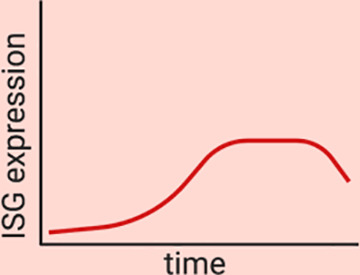
Low magnitude of ISG induction (46–48, 83, 85) Slow but sustained induction of ISGs (46–48, 83, 85)
|
| Negative regulators |
USP18 downregulates IFN-mediated signaling (77, 79, 81) SOCS1 and 3 downregulate IFN-mediated signaling (74–76)
|
|
| IFN-specific ISGS |
|
|


