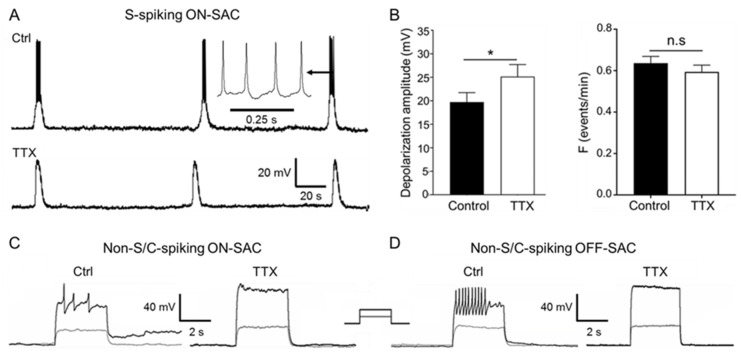
Figure 5.
TTX blocking spontaneous APs and current-induced spikes in SACs. ON- and OFF-SACs from flat-mount retinas of ChAT-Cre/tdTomato mice were recorded from P3 to P7 using a whole-cell current-clamp configuration. (A) APs (see the insert) were superposed onto an S-spiking ON-SAC experiencing spontaneous depolarization in the control (top trace), but they were eliminated in the presence of 0.3 µM TTX (bottom trace) at P5. (B) 0.1–0.5 µM TTX blocked spontaneous depolarization-induced APs in S-spiking ON-SACs recorded from P3 to P7. Pooled data demonstrated that TTX significantly increased the peak amplitude of spontaneous depolarization (left panel, n = 10, * p < 0.05, mean ± SEM) but did not significantly change (n.s.) the frequency of spontaneous depolarization (right panel, n = 10, p = 0.38, mean ± SEM). (C) In a non-S-spiking ON-SAC at P5, current-induced APs (left panel) were blocked by 0.3 µM TTX (right panel). (D) In a non-S-spiking OFF-SAC at P4, current-induced APs (left panel) were blocked by 0.3 µM TTX (right panel). The insert for (C,D) illustrates the injected currents (gray: 200 pA, black: 250 pA) of 500 ms.