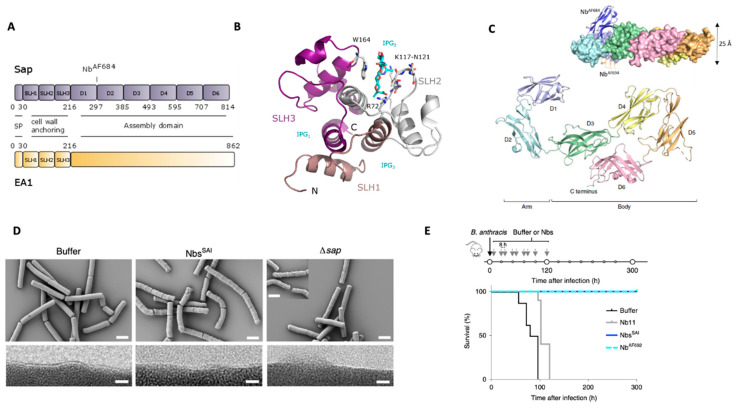
Figure 3.
S-layer architecture of B. anthracis. (A) Domain architecture of Sap and EA1 S-layer proteins. The N-terminal ~216 residues comprise a signal peptide (SP) and a pseudo-repeat of three SLH motifs that form a cell-wall-anchoring domain. Sap assembly domain comprises of 6 independent domains as demonstrated by SapAD crystal structure reported in Fioravanti et al., 2019 (PDB: 6HHU [19]). The site where the therapeutic nanobody AF684 is binding as in upper C panel is indicated (PDB: 6QX4 [19]). (B) Crystal structure of the cell-wall anchoring domain of Sap in complex with a synthetic SCWP unit (IPG). Each of the 3 SLH motifs are highlighted forming a pseudo-trimer shaping 3 SCWP-binding grooves (IPG1-3). Residues important in SCWP binding are highlighted. The S-layer is oriented away from the image plane (C-terminus) with the N-terminus and terminal SCWP unit facing toward us (PDB: 6BT4 adapted from [56]. (C) X-ray structure of SapAD (residues 216–814) of Sap showing an arm-and-body organization composed of 6 β-sandwich domains. The inset shows the nanobodies used to solve the crystal structure. Notable NbAF684, which is binding the hinge region displays therapeutic activity. (D) Scanning and transmission electron microscopy (SEM and TEM, top and bottom row, respectively) representing the morphology defect of B. anthracis 34F2 cells treated with buffer or Sap assembly inhibitory nanobodies (NbsSAI), as well as RBA91 cells (Δsap) treated with buffer. RBA91 and cells treated with NbsSAI present a scoured phenotype. TEM images show the loss of the ordered surface monolayer in RBA91 and in NbsSAI-treated cells. Scale bars, 2 μm and 10 nm for SEM and TEM images, respectively (adapted from Fioravanti et al., 2019). (E) Schematic of the treatment regime and survival curves (bottom) of B. anthracis infection and Nb treatment studies in mice. The treatment consisted of a 6 days course of 10 subcutaneous 100 μL doses of 200 μM Nbs or buffer after infection. Mice receiving buffer or Nb11 (a non-related S-layer Nbs) injections would succumb to lethal anthrax within ~110 h post infection; mice receiving NbsSAI or NbAF692 (the most potent NbsSAI) treatment are able to recover from the infection and survive anthrax disease. n = 8 mice per group. From Fioravanti et al., 2019.