Figure 6.
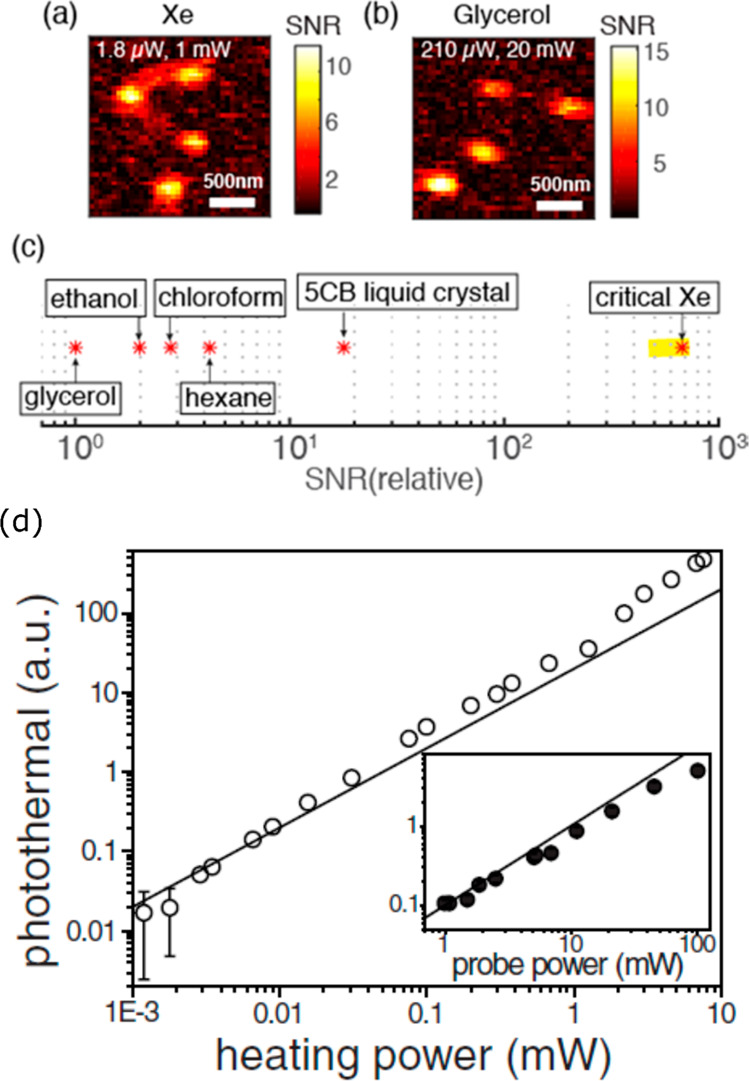
Photothermal images of 5 nm gold nanoparticles in (a) near-critical xenon and (b) glycerol. The heating and probe powers are mentioned. (c) Relative (with regard to glycerol) photothermal signal-to-noise ratio in near-critical xenon (Xe) is compared with other organic solvents and 5CB liquid crystal. The data for the organic solvents are taken from ref (94), and the data for the 5CB liquid crystal taken from refs (27) and (96). Organic solvents such as chloroform, hexane, pentane, and toluene provide a photothermal SNR much higher than that of water or even than that of glycerol because of their low boiling points and the ensuing higher values of their thermorefractive coefficients. The liquid crystal 5CB and critical xenon provide photothermal SNR more than 1 order of magnitude and 2 orders of magnitude, respectively, larger than that of glycerol. (d) Linear power dependence of the photothermal signal with the heating and probe powers. The measurements were performed on a single 20 nm gold nanosphere in glycerol. The solid lines are the linear fits for low powers. The error bars indicate standard deviations. For most data, the error bars are smaller than the symbol size. The linear power dependence of heating and probe beams allows optimization of photothermal signals by tuning the laser powers. The left (a–c) and right (d) figures are adapted with permission from the refs (95) and ref (22), respectively. Copyright 2016 American Chemical Society and copyright 2010 The American Association for the Advancement of Science, respectively.
