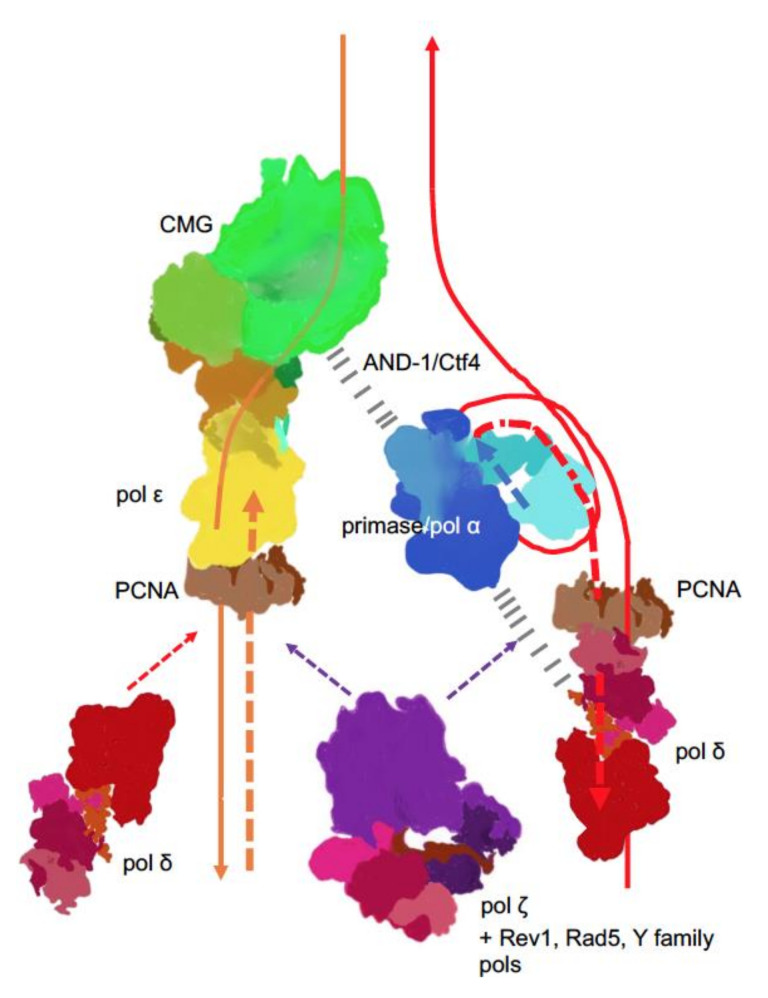
Figure 4.
Main players at the eukaryotic replication fork. The CMG complex unwinds DNA, primase-Pol α synthesizes short RNA-DNA primers that are extended by pol δ. On the lagging strand, pol δ synthesis is halted when the pol reaches the previous Okazaki fragment. On the leading strand, pol ε takes over and contributes to around 80% of the bulk strand synthesis. Pol δ occasionally proofreads errors made by pol ε [25] and likely continues synthesis on the leading strand thereafter. The coordination of the whole process is likely achieved by interactions of primase-pol α with CMG via Ctf4 (yeast) or AND-1 (humans) [93,94,95,96] and some not precisely mapped pol α interactions with pol δ (dashed black lines) [97,98,99]. Replication stress caused by unusual DNA structures [100], DNA damage or defects in replisome [101,102,103,104] lead to recruitment and patches of synthesis of the fourth member of the B-family, pol ζ [105], along with translesion pols and accessory factors to mitigate replication problems, depending on the nature of replication problems.