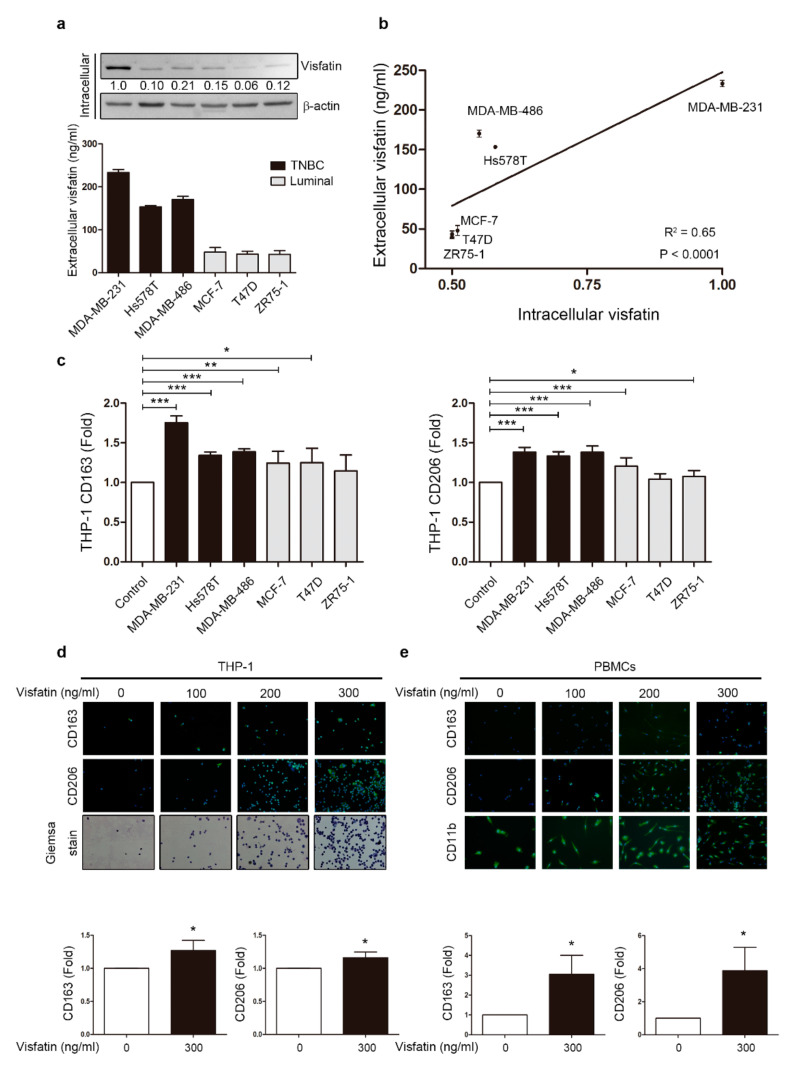
Figure 1.
Breast cancer cell-derived visfatin induced THP-1 and PBMCs differentiation. (a) Breast cancer cells were harvested after culture for 48 h, and intracellular visfatin expression was analyzed by Western blot and extracellular visfatin level by ELISA. Breast cancer cells included triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells (MDA-MB-231, Hs578T, and MDA-MB-486) and luminal breast cancer cells (MCF-7, T47D, and ZR75-1). (b) Correlation between intra/extracellular visfatin was analyzed, with each point representing one breast cancer cell line. (c) Conditioned medium (CM) refers to the medium collected after breast cancer cell culture. Human monocytic cell line THP-1 was treated with CM from various breast cancer cell lines for six days, and M2 markers CD163 and CD206 were analyzed by flow cytometry. (d) THP-1 cells were treated with visfatin at different doses (0, 100, 200, 300 ng/mL) for six days, and M2 markers CD163 and CD206 were detected in attached cells by immunofluorescence staining. Giemsa stain was used to identify macrophages. (40×) (e) PBMCs were treated with visfatin at different doses (0, 100, 200, 300 ng/mL) for six days, and M2 markers CD163 and CD206 were detected in attached cells by immunofluorescence staining, with CD11b as a macrophage marker. Statistical analysis was performed using the t-test and the correlation analysis by linear regression (40×). p-value ≤ 0.05 marked as *; p-value ≤ 0.01 marked as **; p-value ≤ 0.001 marked as ***.