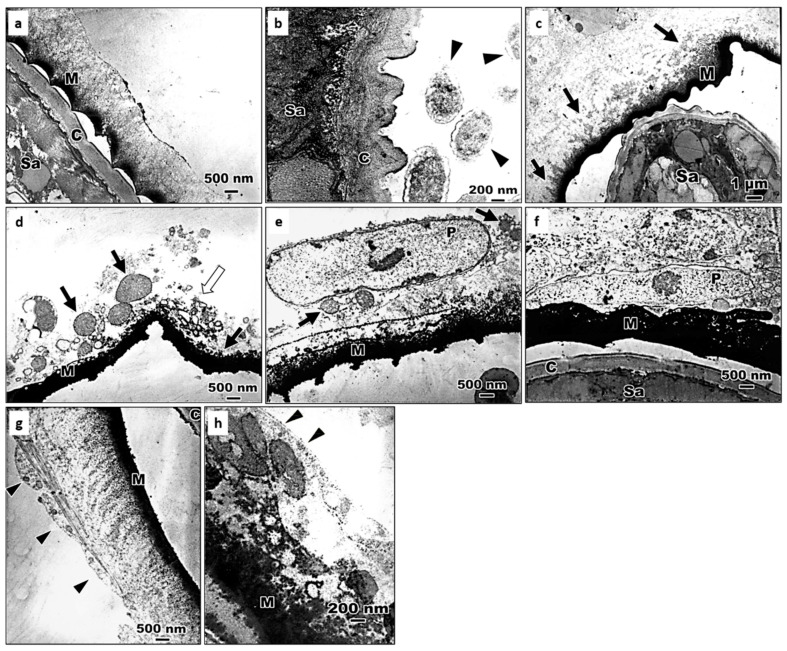
Figure 5.
Electron micrographs showing the process of encapsulation of S. abbasi in the 4th instar larvae of Ae. albopictus. (a) At 10 min after inoculation, melanotic capsule deposited on the surface. C: the cuticle of S. abbasi; M: melanotic capsule; Sa: S. abbasi. (b) At 10 min after inoculation, the electron-condense homogeneous material attached to the cuticle of S. abbasi and symbiotic bacteria-like structures around S. abbasi in the hemocoel of 4th instar larvae. Arrow head (▲): bacteria-like structures; Sa: S. abbasi. C: the cuticle of S. abbasi. (c) At 30 min after inoculation, the inner electron-dense material thickened. Arrows (↑): the electron-condense homogeneous materials; M: melanotic capsule; Sa: S. abbasi. (d) At 1 h after inoculation, cell debris appeared on the out layer of humoral capsule. Black arrows (↑): mitochondria; White arrows (↑): cell debris; M: melanotic capsule. (e) At 1 h after inoculation. M: melanotic capsule; P: plasmatocyte; Arrows (↑): mitochondria. (f) At 2 h after inoculation, plasmatocyte on the melanotic capsule. C: the cuticle of S. abbasi; M: melanotic capsule; P: plasmatocyte; Sa: S. abbasi. (g) At 24 h after inoculation, intact hemocytes appeared on the humoral capsule. Arrow head: a hemocyte. (h) At 48 h after inoculation, the basement membrane-like structures between cellular capsule and hemocoel. Arrow head: the basement membrane-like structures.