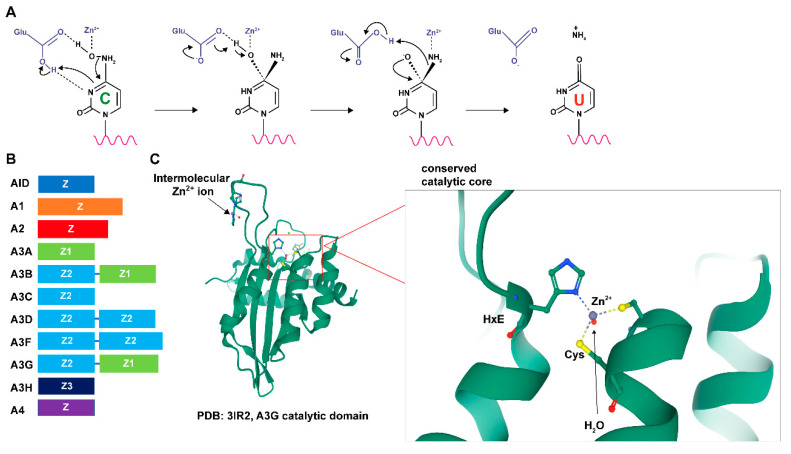
Figure 1.
Structural characteristics and activity of APOBECs. (A) Reaction of APOBEC-mediated cytidine deamination (see text for details). (B) Different APOBECs are composed of distinct zinc-coordinating (Z) domains. In the mammalian A3 family, Z domains are categorized into three distinct phylogenetic groups, Z1, Z2, and Z3. Members of the human APOBEC genes and the relative lengths of their Z domains are shown. (C) A ribbon diagram of the A3G catalytic domain shows its globular structure and an expanded view of the zinc-coordinating active site (from PDB 3IR2) [10]. Zinc ions are depicted in gray. The expanded view shows the interactions of the histidine ring and cysteine side chains with zinc. The red dot near the zinc ion represents a water molecule.