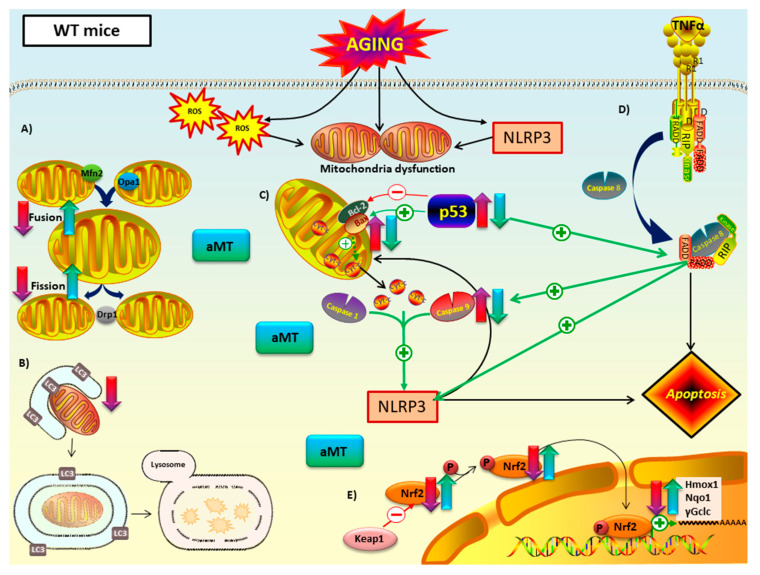
Figure 9.
Proposed mechanism of melatonin in mitochondria of WT mice during cardiac aging. (A) Mitochondrial dynamics: aging led to a decline in fusion (Mfn2 and Opa1) and fission proteins (Opa1). Melatonin treatment counteracted this decrease. (B) Autophagy (mitophagy): autophagic capacity dropped in aged myocardium. Melatonin therapy had minimal impact on this pathway. (C) Intrinsic and (D) extrinsic apoptosis: WT mice have intrinsic and extrinsic pathways mediated by p53 and caspase 9. Those apoptotic markers, as well as Bax/Bcl2 ratio, increased with aging and are related with NLRP3 activation. This inflammasome seemed to have a regulatory effect on the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, which depends on mitochondria cytochrome c release. Melatonin supplementation had an anti-apoptotic effect in both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis. (E) Nrf2-dependent antioxidant response: Nrf2 and pNrf2 (Ser40) were reduced with aging. This loss was linked to the decrease of the cytoprotective enzyme transcriptionally regulated by Nrf2: Hmox1, Nqo1 and γGclc. Melatonin recovered this antioxidant pathway. No changes in Keap1 were reported. Red-purple arrow: impact of aging. Green-blue arrow: effect of melatonin treatment.