Table 1.
NMDAR channel blockers and their effects on gating.
| Compound | Structure | Type of Blocker | Effects on Gating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnesium |
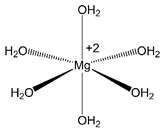
|
Unclear—due to fast unblocking kinetics, trapping of Mg2+ has not been directly demonstrated. | None [13,202]. |
| 9-aminoacridine |
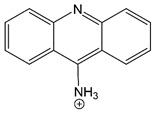
|
Sequential [7,201]. | Stabilizes open state [7,201]. Prevents agonist dissociation [7,201]. |
| IEM-1754 |
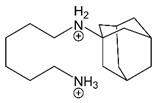
|
Depolarized potentials: sequential [173]. Strongly negative potentials: trapping [173]. |
Depolarized potentials: Stabilizes open state [173]. |
| Amantadine |
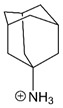
|
Partial trapping [12,13]. | Accelerates channel closure of native NMDARs and GluN1/2B receptors [8]. |
| Memantine |
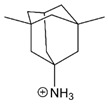
|
Partial trapping [8,16,197,203,204]. | Slows GluN1/2A receptor recovery from Ca2+-dependent desensitization [3]. |
| Ketamine |
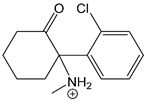
|
Trapping [204]. | Accelerates GluN1/2B receptor recovery from desensitization [3]. |
Magnesium is depicted coordinating six water molecules, and all organic blockers are depicted in bond-line format. Blockers structures are scaled to depict approximate relative sizes.
