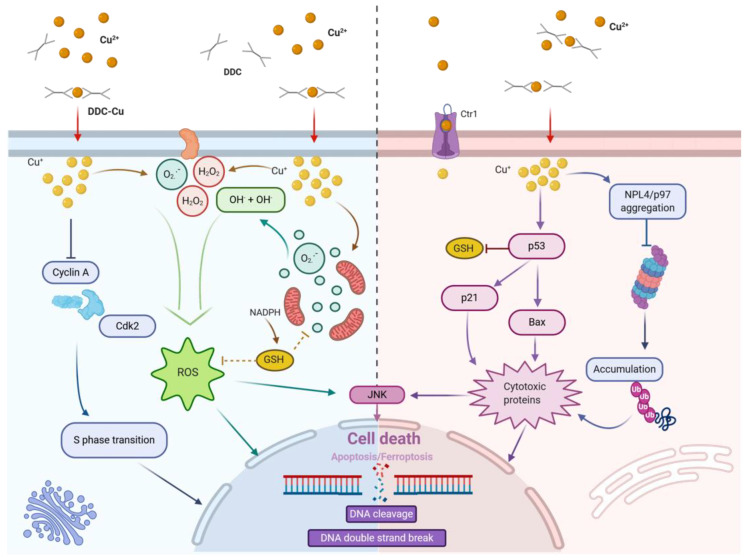
Figure 2.
Mode of action of disulfiram-derived diethyldihtiocarbamate (DDC) on cancer cells. Cellular uptake of DDC-Cu2+ causes an increase in the free copper pool (Cu+) which provokes massive induction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that have a vast range of effects, including the induction of DNA damage (left). At the same time, the copper accumulation leads to the activation of p53 signalling, dysfunction of proteasomal removal of poly-ubiquitinylated proteins, activation of stress-activated protein kinases like JNK and the induction of death pathways (right).