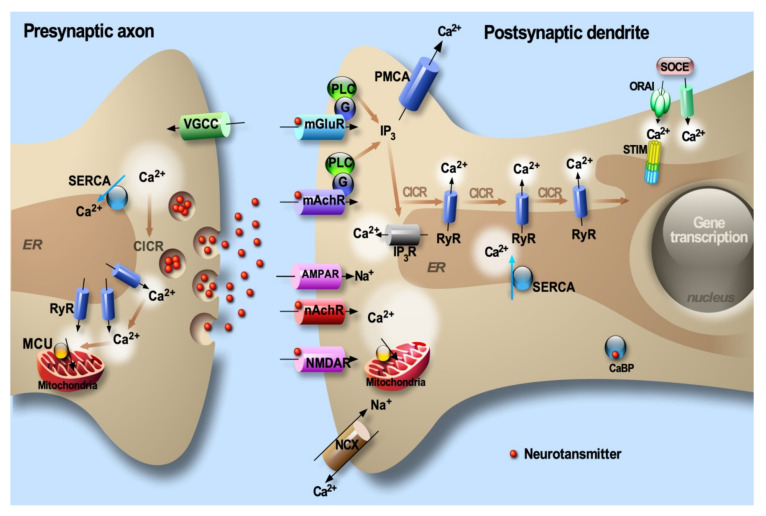
Figure 1.
Elevations of intraneuronal [Ca2+] are the result of an influx across the plasma membrane and the release from the ER through various channels and receptors. The low intraneuronal Ca2+ level is then maintained by the activity of Ca2+-binding proteins (CaBP) and involves the sodium-Ca2+ exchanger (Na+/Ca2+) acting in concert with the ATP-dependent Ca2+ pumps located at the plasma membrane and the ER. Depletion of ER Ca2+ content activates the store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) pathway.