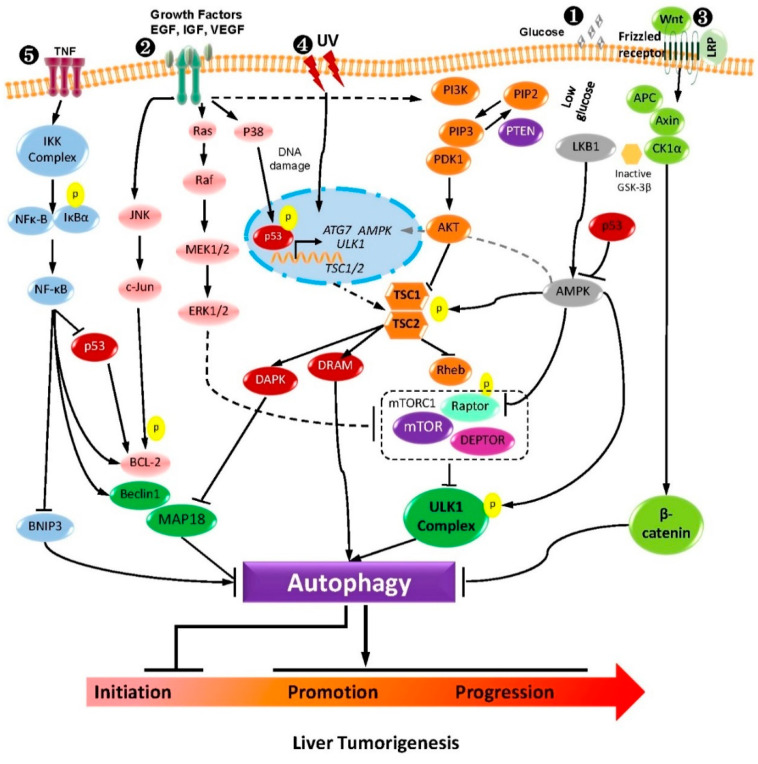
Figure 2.
The crosstalk between the major signaling pathway regulating autophagy and liver tumorigenesis. (1) PI3K-AKT-mTOR and AMPK-mTOR pathway receptor tyrosine kinases promote the conversion of PIP2 to PIP3 and the activation of PI3K. Activation of AKT by dephosphorylation of PIP3 caused by PTEN could negatively regulate PI3K signaling. Amino acids and nutrient-rich conditions initiate mTORC1 activation. In comparison, starvation and oxidative stress inhibit mTORC1 activation and induce autophagy. AMPK regulates autophagy either by phosphorylating TSC via the mTOR pathway or by directly phosphorylating ULK1. (2) EGFR, IGF, and MAPK pathway EGFR family members contribute to autophagy by activating three of the major signaling pathways for cell survival via the regulation of the autophagy process JNK/c-Jun, Ras/Raf, and the PI3K/AKT pathway. (3) Wnt-β-catenin pathway: This pathway results in the activation and nuclear recruitment of β-catenin protein, leading to directly regulating autophagy. In the canonical Wnt pathway, without Wnt β-catenin is degraded by a destruction complex and would not accumulate in the cytoplasm. This destruction complex consists of the following proteins: Axin, adenomatosis polyposis coli (APC), protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3), and casein kinase 1α (CK1α). (4) p53 pathway: Autophagy is also mediated by nuclear p53 activity, a transcription factor in stress conditions, such as UV, etc. p53 primarily induces the canonical pathway of autophagy by PI3K-AKT-mTOR, AMPK-mTOR, and ULK1 complex. Alternatively, damage-regulated autophagy modulator (DRAM), death-associated protein kinase (DAPK), or ATG7 upregulation by the p53 can also initiate autophagy. (5) NFκ-B pathway IKKα/β and NF-κB induce autophagy by increasing the Beclin 1 and other autophagy-related proteins’ expression levels. Moreover, increased autophagy can degrade IKK components and repress autophagy. Besides this, NF-κB signaling could inhibit autophagy by the over-expression of autophagy repressors, such as Bcl-2/Xl and BNIP3.