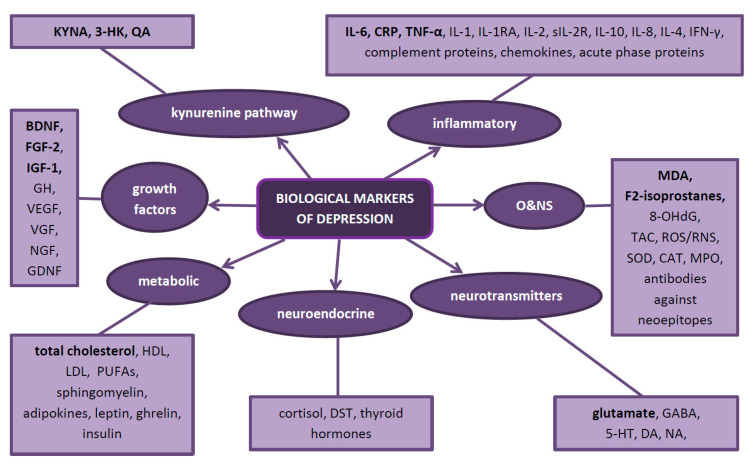
Figure 2.
The summary of the most important depression markers. In bold—those confirmed by a recent umbrella meta-analysis [40]. Abbreviations: 3-HK—3-hydroxykynurenine; 5-HT—serotonin; 8-OHdG—8-hydroxy-2-deoxiguanosine; BDNF—brain-derived neurotrophic factor; CAT—catalase; CRP—C-reactive protein; DA—dopamine; DST—dexamethasone suppression test; FGF-2—fibroblast growth factor-2; GABA—gamma-aminobutyric acid; GDNF—glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor; GH—growth hormone; HDL—high-density lipoprotein; IGF-1—insulin-like growth factor-1; IL-1—interleukin-1; IL-2—interleukin-2; IL-4—interleukin-4; IL-6—interleukin-6; IL-8—interleukin-8; IL-10—interleukin-10; IL-1RA—interleukin-1 receptor antagonist; INF-γ—interferon-γ; KYNA—kynurenic acid; LDL—low-density lipoprotein; MDA—malonylo-dialdehyde; MPO—myeloperoxidase; NA—noradrenaline; NGF—nerve growth factor (NGF); O&NS—oxidative and nitrosative stress; PUFAs—polyunsaturated fatty acids; QA—quinolinic acid; ROS/RNS—reactive oxygen/nitrogen species; sIL-2R—soluble interleukin-2 receptor; SOD—superoxide dismutase; TAC—total antioxidant capacity; TNF-α—tumor necrosis factor-α; VEGF—vascular endothelial growth factor; VGF—VGF nerve growth factor.