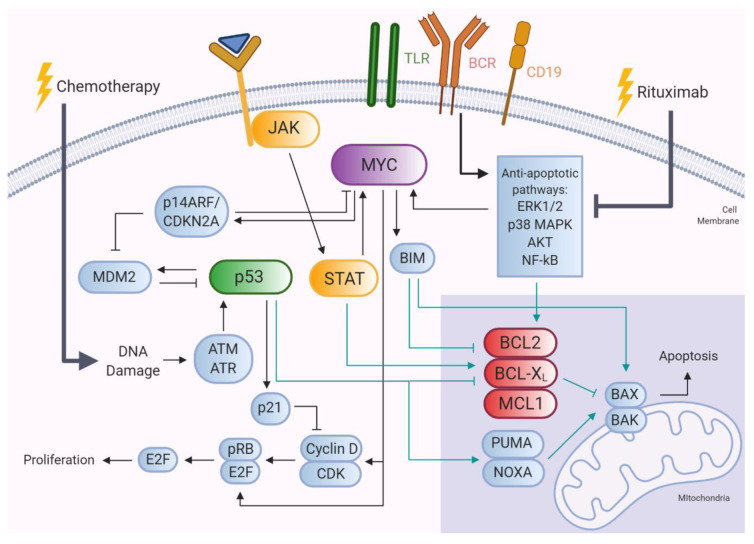
Figure 1.
Relapse-associated genes and pathways interacting with R-CHOP immunochemotherapy. DNA damage induced by chemotherapy activates the p53 pathway, thereby inhibiting cell proliferation by p21 upregulation and inducing apoptosis through regulation of BCL2-members. Rituximab inhibits several anti-apoptotic pathways leading to downregulation of anti-apoptotic BCL2 members, and regulation of MYC. MYC, in its turn, exerts multiple functions, including regulation of the p53 pathway and pro-apoptotic executioner proteins, BAX and BAK, and the cell cycle. Activation of the JAK-STAT pathway affects proliferation and apoptosis of lymphoma cells. TLR, Toll-like receptor; BCR, B cell receptor. Turquoise lines indicate regulation of the BCL2 family members.