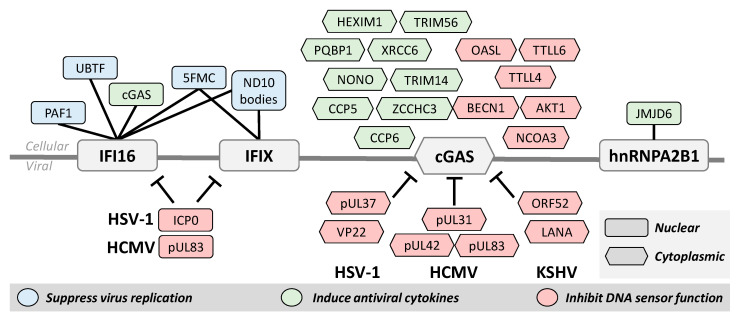
Figure 3.
Protein–protein interactions contribute to the activation or inhibition of DNA sensor. Over the course of viral infection and immune signaling, DNA sensors interact with other cellular and viral proteins. Several of these cellular proteins are important for the function of the DNA sensors for both suppressing virus replication by repressing viral transcription and inducing antiviral cytokines. Protein interactions are also used to regulate DNA sensor function. Viruses have evolved distinct mechanisms to facilitate immune evasion and cells must also possess mechanisms to prevent excessive immune signaling. Although localized to both the nucleus and cytoplasm, protein interactions with cGAS are best characterized in the cytoplasm. Nuclear proteins are shown here as rectangles and cytoplasmic interactions as hexagons.