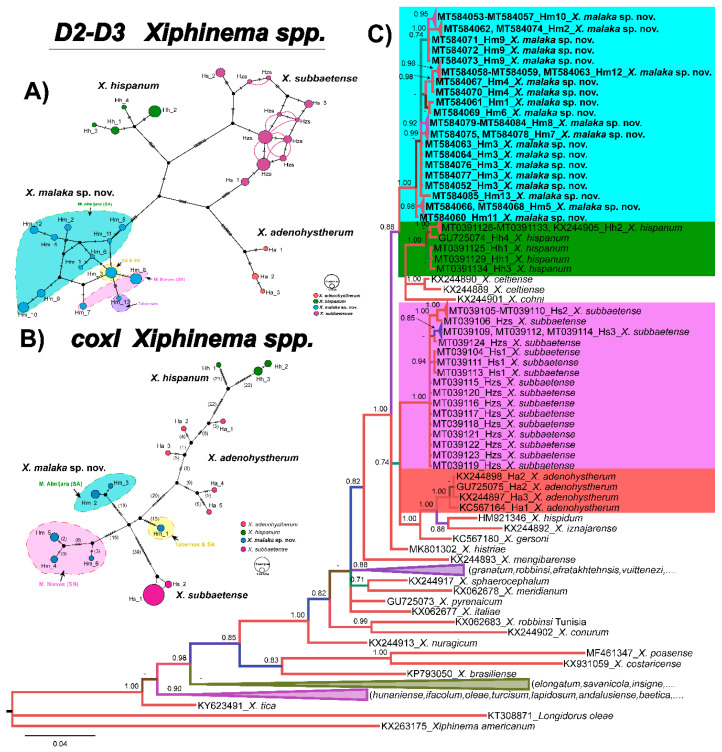
Figure 3.
(A). Construction of D2-D3 haploweb of Xiphinema malaka sp. nov. (B). coxI haplonet of Xiphinema malaka sp. nov. Coloured circles represent haplotypes and their diameter are proportional to the number of individuals sharing the same haplotype. Black short lines on the branches indicate the number of mutated positions in the alignment that separate each haplotype. Co-occurring haplotypes are enclosed in black dashes. (C). Phylogenetic relationships within the genus Xiphinema. Bayesian 50% majority rule consensus tree as inferred from D2 and D3 expansion domains of 28S rRNA sequence alignment under the general time-reversible model of sequence evolution with correction for invariable sites and a gamma-shaped distribution (GTR + I + G) +. Posterior probabilities more than 0.70 are given for appropriate clades. Newly obtained sequences in this study are shown in bold. Scale bar = expected changes per site. Some branches were collapsed for improving readability of Xiphinema species. Abbreviations: Ha = X. adenohystherum haplotypes; Hh = X. hispanum haplotypes; Hm = X. malaka sp. nov. haplotypes; Hs = X. subbaetense haplotypes; Hzs = X. subbaetense heterozygous specimens. SA = Mountain of Almijara and Tejeda; SN = Mountain of Nieves.