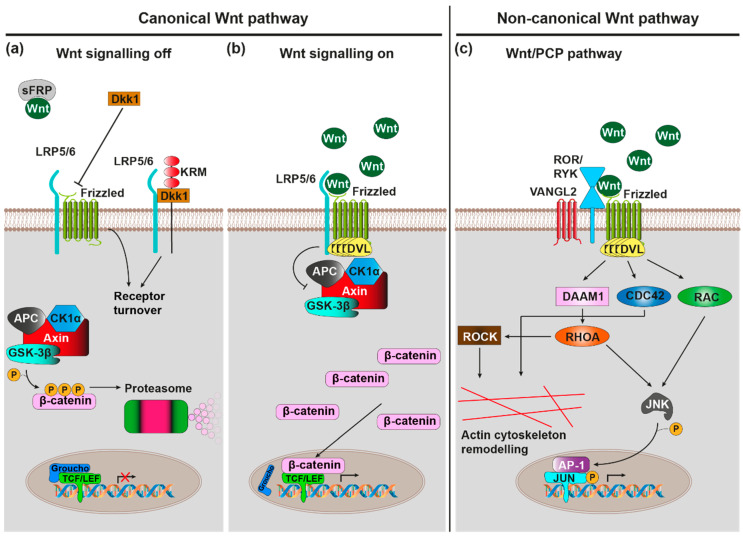
Figure 1.
Wnt signalling pathways. Note that emphasis is placed on pathways and components that are of greater relevance in the context of AD. (a) Canonical Wnt signalling pathway, off: In absence of Wnt ligand binding to Frizzled (Fz)-LRP5/6 heterodimeric cell surface receptors, the Axin/APC/CK1α/GSK-3β destruction complex phosphorylates the transcription factor β-catenin, marking it for proteasomal degradation. Endogenous canonical Wnt antagonists (including sFRP and Dkk1) further favour the ‘off’ state. (b) Canonical Wnt signalling pathway, on: Wnt ligand binding to Fz-LRP5/6 recruits the scaffolding protein DVL, which in turn inhibits GSK-3β activity of the destruction complex. β-catenin subsequently accumulates in cytoplasm, allowing it to translocate to the nucleus where it transactivates the TCF/LEF-mediated expression of canonical Wnt target genes. (c) Wnt/planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway: Wnt ligand binding to Fz-ROR/RYK co-receptors recruits DVL, which in turn activates the small GTPases RHOA, RAC, and CDC42. RHOA and RAC conjointly activate JNK, which stimulates Jun transcription factor dependent gene expression via phosphorylation. Furthermore, RHOA, via ROCK, and CDC42 stimulate actin cytoskeleton remodelling.