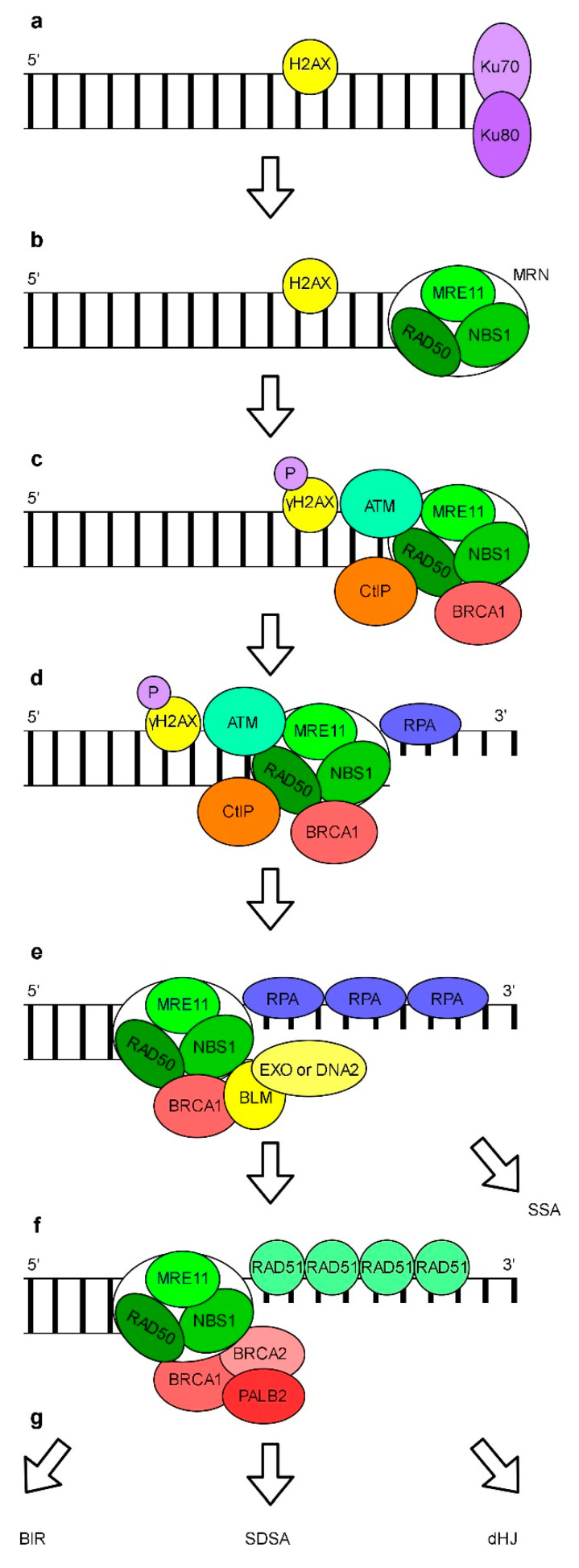
Figure 6.
A simplified mechanism of homologous recombination based on a mammalian model. The DNA termini of DSBs are coated by the Ku70/80 complex (a). The MRN complex, composed of MRE11, RAD50 and NBS1 replaces Ku70/80 (b). MRN recruits ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM), which phosphorylates histone H2AX positioned close to the site of a break. BRCA1 and CtIP are recruited (c). MRN with BRCA1 and CtIP promote a short resection of the free 5′ DNA end creating a 3′ overhang, which is coated by RPA (d). BLM and EXO1 or DNA2 are recruited and generate a longer 3′ overhang which is coated with RPA (e). The BRCA1-PALB2-BRCA2 complex promotes a replacement of RPA by RAD51 monomers and the formation of a RAD51 filament (f). The repair is completed by the BIR (break-induced replication), SDSA (synthesis-dependent strand annealing) or dHJ (double Holliday junctions) pathways (g) and alternatively by the SSA (single-strand annealing) pathway after the resection of DNA by BLM and EXO1 or DNA2 (e).