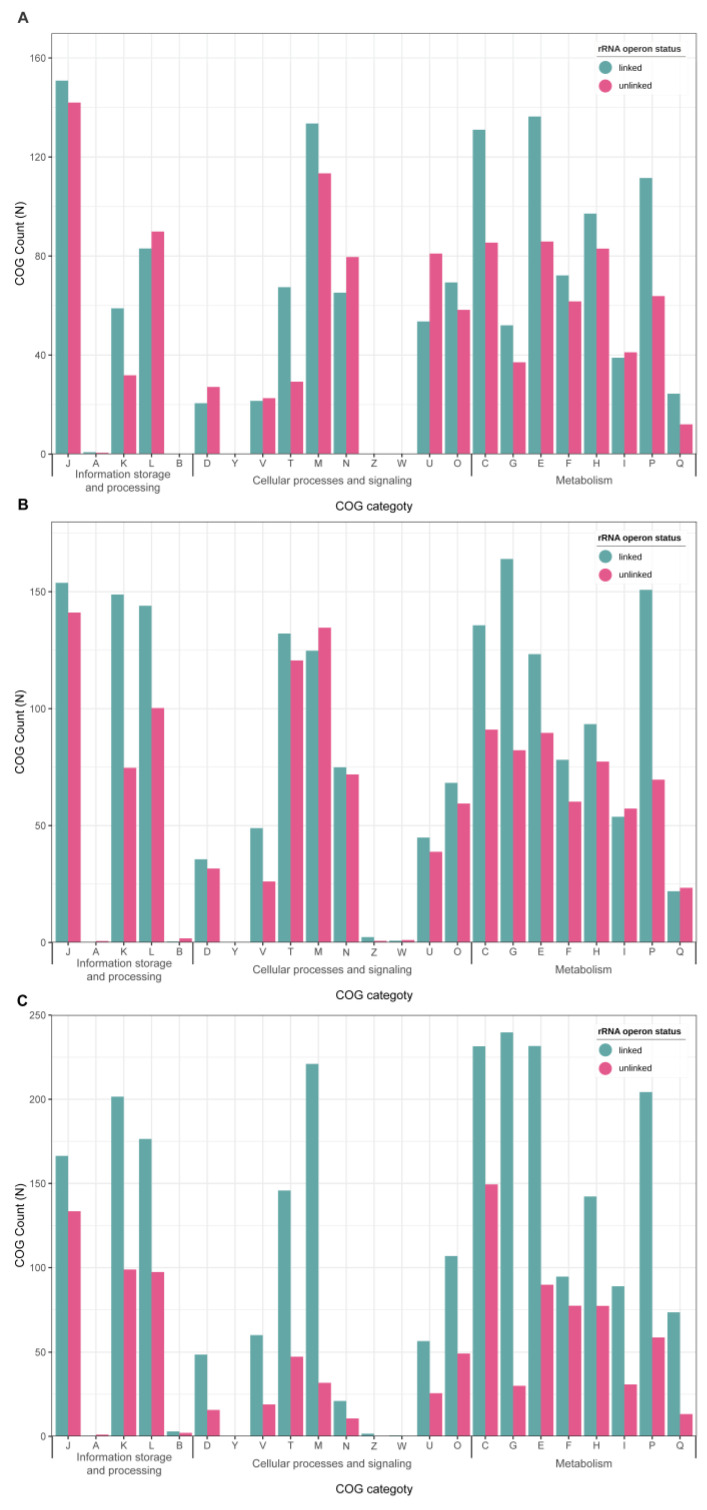
Figure 7.
Quantitative abundance of Clusters of Orthologous (COG) categories between linked and unlinked genomes. Mixed genomes are excluded, and the average number of each group is shown. (A) Campylobacterota; (B) Spirochaetota; (C) Chloroflexota. COG functional categories: J, Translation, ribosomal structure, and biogenesis; A, RNA processing and modification; K, Transcription; L, Replication, recombination, and repair; B, Chromatin structure and dynamics; D, Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning; Y, Nuclear structure; V, Defense mechanisms; T, Signal transduction mechanism; M, Cell wall/membrane/envelop biogenesis; N, Cell motility; Z, Cytoskeleton; W, Extracellular structures; U, Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport; O, Post-translational modification, protein turnover, chaperones; C, Energy production and conversion; G, Carbohydrate transport and metabolism; E, Amino acid transport and metabolism; F, Nucleotide transport and metabolism; H, Coenzyme transport and metabolism; I, Lipid transport and metabolism; P, Inorganic ion transport and metabolism; Q, Secondary metabolite biosynthesis, transport, and catabolism.