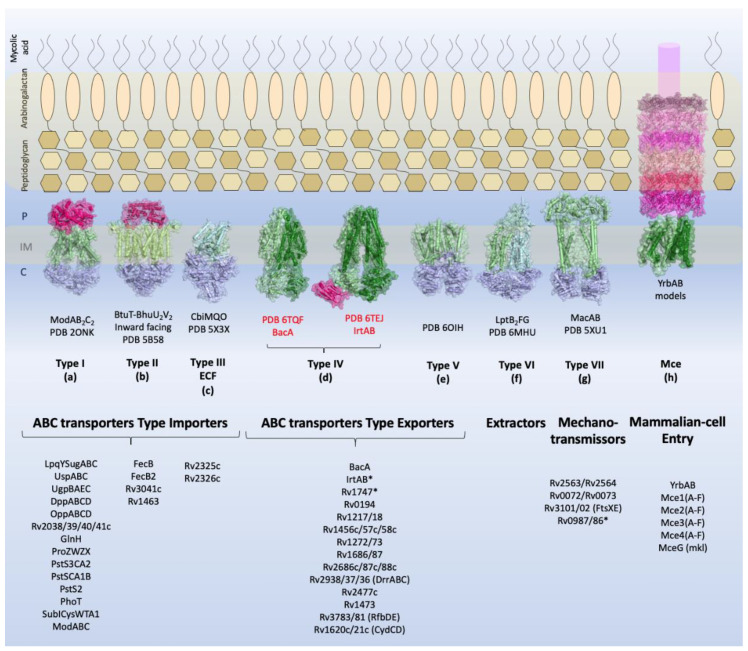
Figure 1.
Overview of the types of ABC transporters and the components identified in M. tuberculosis. Schematic view of the M. tuberculosis cellular envelope is shown with the families of TMDABC transporters organized into importers (Types I–III), exporters (Types IV and V), extractors, and mechanotransmitters. Additionally, the structural representation of the Mce complex (Mammalian-cell entry proteins), which has two ABC-like TMDs, is shown. Representative structure of each transporter class is shown in the inner membrane: Type I, the molybdate transporter ModABC of Archaeoglobus fulgidus (PDB 2ONK); Type II, the vitamin transporter BtuT-BtuUV of Burkholderia cenocepacia (PDB 5B58); Type III, the cobalt energy-coupling factor transporter CbiMQO of Rhodobacter capsulatus (PDB 5 × 3X); Type IV, two ABC transporter type exporter of M. tuberculosis that had the three-dimensional structure resolved are shown: the ABC transporter of vitamin B12, BacA (gene Rv1819c) (PDB 6TQF), and the transporter of siderophores, IrtAB (PDB 6TEJ) (nomenclature in red); Type V, the transporter of O-antigen of Aquifex aeolicus VF5 (PDB 6OIH); Type VI, Cryo-EM structure of the E. coli LptB2FG transporter (PDB 6MHU); Type VII, the structure of MacAB-like efflux pump from Streptococcus pneumoniae (PDB 5XU1); Mce complex, prediction of the structural organization of Mce transporter systems (Mce1-4); the two ABC components, YrdAB, and the periplasmic domains, proteins MceA to MceF were modelled using I-Tasser server [8] based on E. coli Mla components. The structures are shown in cartoon representation with a transparent surface. The substrate-binding proteins from Type I importers and the periplasmic domains of Mce complex are shown in pink shades; the transmembrane domains are shown in dark and pale green, and the nucleotide-binding domains are shown in blue. P: periplasm, IM: inner membrane, C: cytoplasm. The ABC transporters and components of M. tuberculosis described in this review are listed below the representative structures. Transporters marked with asterisk (*) have structural organization that does not fit the functional or structural classification.