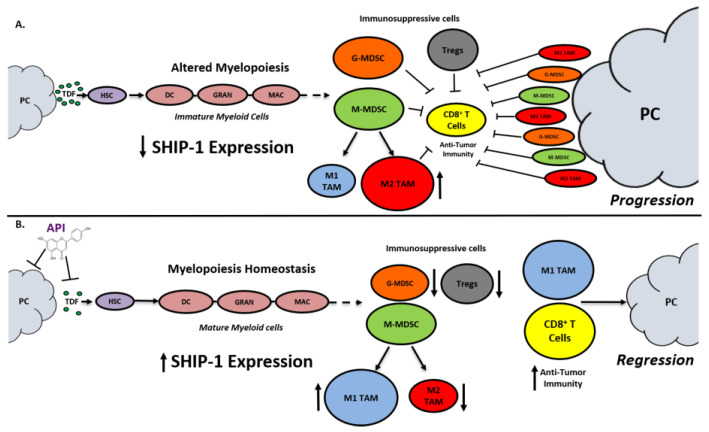
Figure 8.
Proposed Model. Apigenin Increases SHIP-1 Expression, Augments Tumoricidal Macrophages and Improves Anti-Tumor Immune Responses in PC: (A) Pancreatic Tumor Microenvironment without Apigenin (API): Pancreatic cancer cells release tumor-derived factors (TDF) (green) that cause a decrease in SHIP-1 expression. The reduction in SHIP-1 expression causes hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) (purple) to skew towards altered myelopoiesis which yields immature myeloid cells (pink), including dendritic cells (DC), granulocytes (GRAN), and macrophages (MAC). This leads to the expansion of MDSC subsets, G-MDSC (orange) and M-MDSC (light green). M-MDSC mobilizes into the TME and differentiate into more pro-tumor M2-like TAM (red) compared to M1-like TAM (blue). MDSC subsets influence Treg (gray) expansion. MDSC subsets, M2-like TAM and Treg prevent anti-tumor immunity by blocking the migration of effector CD8+ T cells into the TME which leads to tumor progression. (B) Pancreatic Tumor Microenvironment with API: API targets and reduces the production of TDFs (directly or indirectly), leading to increased SHIP-1 expression, which promotes myelopoiesis homeostasis and the development of mature myeloid cells (DC, GRAN, and MAC). These M-MDSC that mobilize to the TME reprogram into tumoricidal M1-like TAM compared to M2-like TAM. Moreover, API treatment leads to a decrease in G-MDSC, M2-like TAM and Treg percentages in the TME. More importantly, API treatment increases the migration of effector CD8+ T cells (i.e., CD3+ TILs) into the TME, which elicits its anti-tumor activity, that causes pancreatic tumor regression.