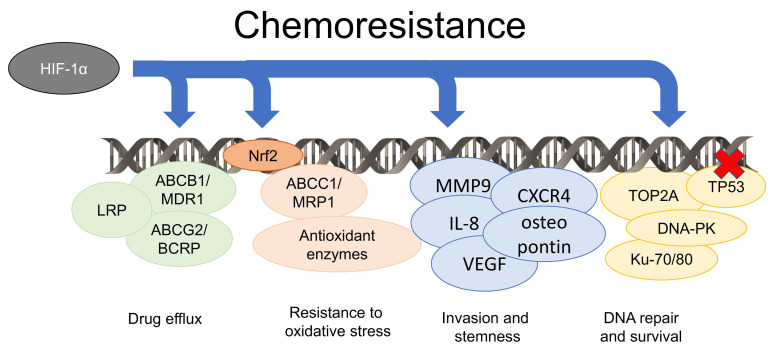
Figure 2.
Metabolism-independent factors determining chemoresistance in hypoxia. HIF-1α transcriptionally induces drug efflux transporters belonging to the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) Binding Cassette (ABC) family, such as ABC transporter B1/multidrug resistance 1 (ABCB1/MDR1, known as P-glycoprotein/Pgp), ABC transporter G2/breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2/BCRP), lung cancer resistance protein (LRP), ABC transporter C1/multi-drugs resistance related protein 1 (ABCC1/MRP1), by cooperating with the transcription factor Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) that also up-regulates anti-oxidant enzymes. Moreover, HIF-1α increases genes that induce the acquisition of a pro-invasive and stem-like phenotype, such as matrix metalloprotease 9 (MMP9), C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), osteopontin, interleukin-8 (IL-8), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and up-regulates genes promoting DNA repair, such as topoisomerase 2A (TOP2A), DNA-protein kinases (DNA-PKs), Ku-70, and Ku-80, inhibits TP53 activity, preventing DNA damage. This complex and coordinated transcriptional program favors cell survival and determines chemoresistance in cancer cells.