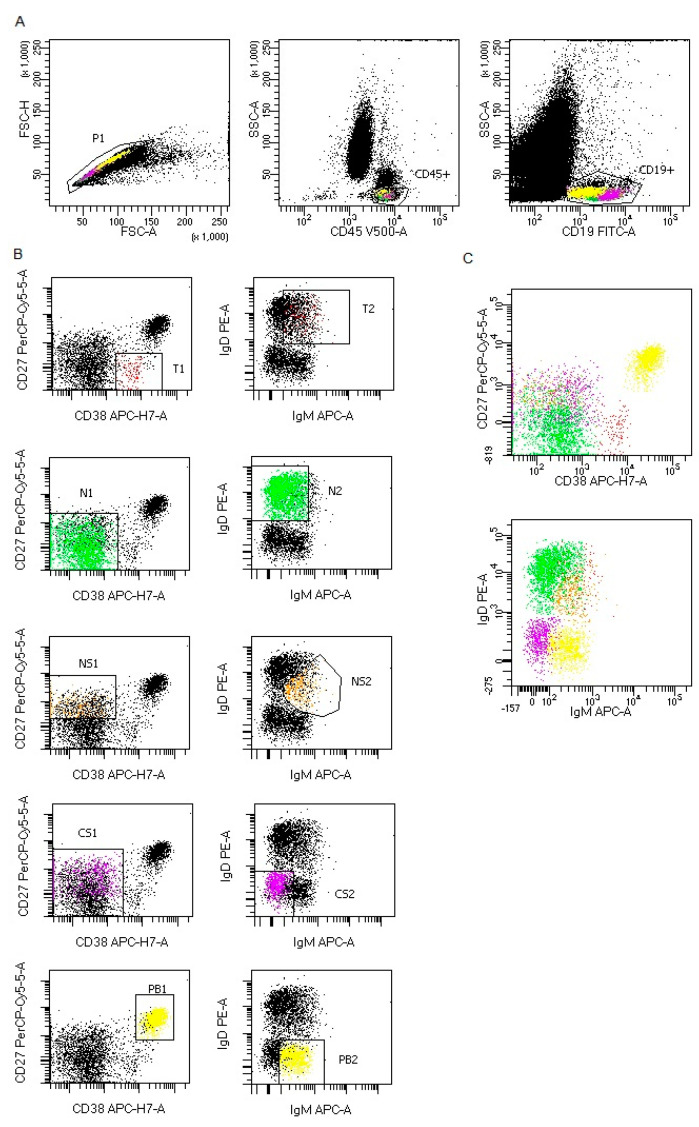
Figure 1.
Representative B lymphocytes maturation gating strategy in COVID-19 patients. (A) B lymphocytes gating strategy: FSC-A vs. FSC-H plot: Gating the cells that have an equal area and height, thus removing clumps (greater FSC-A relative to FSC-H) and debris (very low FSC), CD45 vs. SSC-A plot: Broad selection of lymphocytes based on their SSC/CD45 properties, CD19 vs. SSC-A plot: Broad selection of lymphocytes B based on their SSC/CD19 properties. (B) B lymphocytes maturation gating strategy for each maturation subsets: T1,T2-transitional B cells, N1,N2-naïve B cells, NS1, NS2-non-switched memory B cells, CS1, CS2-class switched memory B cells and PB1, PB2-plasmablasts. (C) representative plots with all B lymphocytes maturation subsets. CD27 vs. CD38 plot: Broad selection of B lymphocyte maturation subsets based on their CD27/CD38 properties, IgD vs. IgM plot: Broad selection of B lymphocyte maturation subsets based on their IgD/IgM properties. Plots show all B lymphocyte maturation subsets: Transitional B cells (red), naïve B cells (green), non-switched memory B cells (orange), class switched memory B cells (purple) and plasmablasts (yellow).