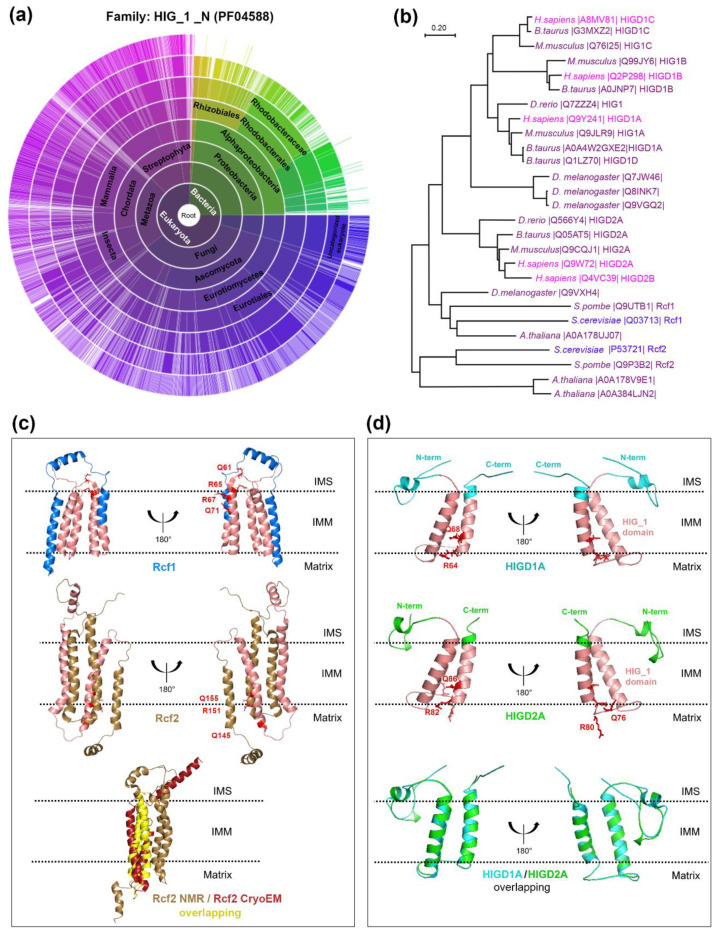
Figure 1.
Distribution of HIG_1_N (PF04588) domain proteins across species. (a) Modified “sunburst” visualization of the taxonomic lineage distribution of 1911 different species that in total have 3472 protein sequences containing the hypoxia-inducible gene (HIG)-1-N domain (Pfam ID: PF04588). The graph shows each node in the tree as a separate arc, arranged radially with the superkingdoms at the center and the species arrayed around the outermost ring. The graph was generated with tools from pfam.xfam.org hosted by the European Bioinformatics Institute at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL-EBI). Yellow-green colors represent different types of bacteria, and purple color represent eukaryotes. (b) Phylogenetic tree of Hypoxia-inducible gene domain (HIGD) proteins across eukaryotic species. The evolutionary history was inferred using the Neighbor-Joining method. We show the optimal tree with the sum of branch length = 8.97673253. The tree was drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed using the Poisson correction method and are in the units of the number of amino acid substitutions per site. This analysis involved 27 amino acid sequences obtained from UniProt and entered manually. All ambiguous positions were removed for each sequence pair (pairwise deletion option). There were a total of 253 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA X [42,43]. (c) Solution NMR structures of S. cerevisiae respiratory supercomplex factors Rcf1 and Rcf2. The top panel shows ribbon diagrams of the Rcf1 structure (Protein database -PDB- code 5NF8), with the HIG_1 domain in salmon. The middle panel shows the Rcf2 structure (PDB 6LUL) [44], with the HIG_1 domain in salmon. The QRRQ motifs in Rcf1 and Rcf2 are marked in red. The lower panel shows the overlapping of the NMR structure of Rcf2 (PDB 6LUL) (in gold) and the partial cryo-EM structure for Rcf2 as bound to hypoxic respiratory supercomplex (SC) CIII2+CIV (PDB 6T15) [34] (in red). The Rcf2 transmembrane helices resolved by NMR that overlap with the Rcf2 cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure are presented in yellow. A prominent difference between the two structures relates to the C-terminal α-helix, shown to protrude into the intermembrane space by cryo-EM. (d) Solution NMR structures of human HIGD1A and HIGD2A. The top panel shows ribbon diagrams of the structure of HIGD1A (PDB 2LOM), with the HIG_1 domain in salmon. HIGD1A is a type 1 HIGD protein, with a truncated QRRQ motif, labeled in red. The middle panel presents ribbon diagrams of the predicted structure of HIGD2A. The structure was predicted in silico using Swiss-Model based on the alignment with HIGD1A, with 0.75 coverage of the sequence [45,46,47]. Residues of the QRRQ motif are labeled in red and HIG_1 domain, in salmon. The bottom panel depicts a superposition view of HIGD1A and HIGD2A structures generated by PyMOL. IMS: intermembrane space. IMM: inner mitochondrial membrane.