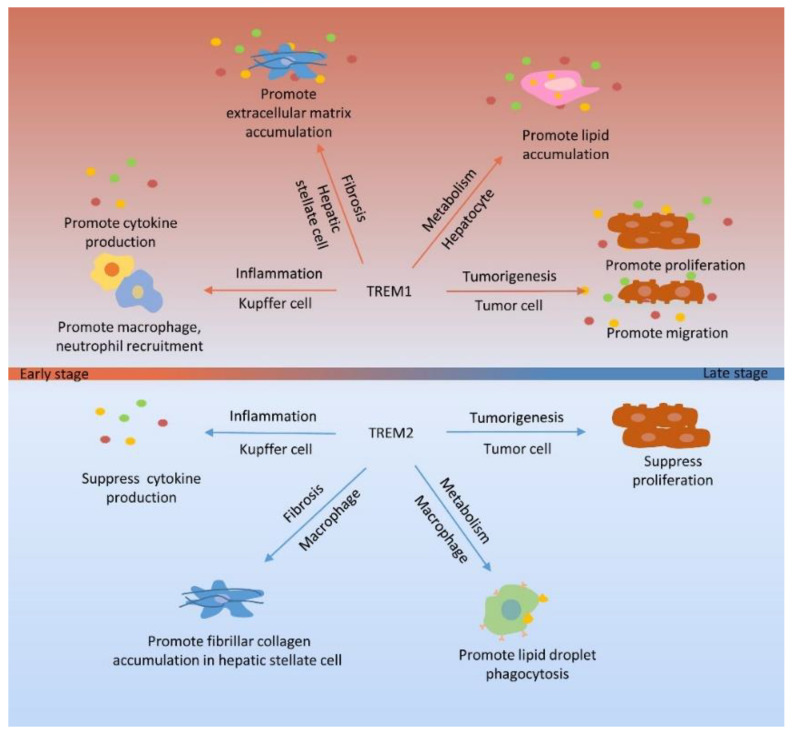
Figure 3.
The biological process of TREM1 and TREM2 involved in liver-related diseases. In the early stage of liver-related diseases, the biological function of TREM1 is dominant. To maintain homeostasis, the biological function of TREM2 gradually occupies a dominant position in the late stage. In the inflammatory response, TREM1 expressed on Kupffer cells upregulates production of cytokines and recruits macrophages and neutrophils, which augments inflammation. However, TREM2 expressed on Kupffer cells suppresses production of cytokines. In fibrosis process, pro-inflammatory response of Kupffer cells induced by TREM1 activates hepatic stellate cells. TREM1 also promotes the deposition of extracellular matrix in hepatic stellate cells. TREM2 expressed on macrophages promotes fibrillar collagen accumulation in hepatic stellate cells. In metabolic regulation, TREM1 expressed on hepatocytes promotes lipid accumulation, which causes lipotoxicity to hepatocytes. TREM2 expressed on macrophages increases the phagocytosis of lipid droplet. In tumorigenesis process, TREM1 expressed on tumor cells promotes proliferation and migration, but TREM2 is to suppress proliferation of tumor cells. TREM, triggering receptors expressed on myeloid cells.