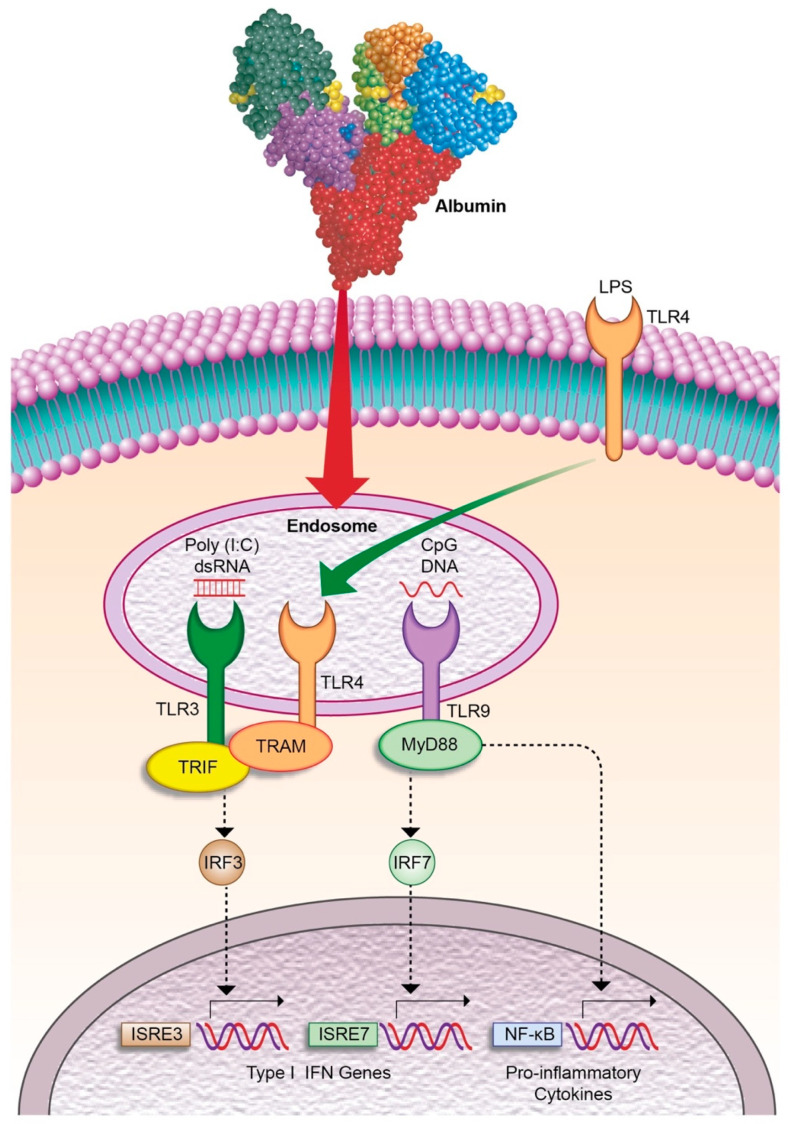
Figure 2.
Human serum albumin (HSA) exerts immunomodulatory effects in leukocytes by blocking Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathways in the endosomal compartment. HSA is internalized by leukocytes and in the endosomes inhibits inflammatory cytokine production induced by bacterial single-strand CpG-DNA, which binds to its cognate receptor TLR9 and triggers the signaling by recruitment of myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88 (MyD88). HSA also inhibits other endosomal TLRs such as TLR3, which is activated by double-strand RNA (i.e., poly (I:C)) and TLR4, which, after binding to LPS, translocates to the endosome. Both TRL3 and TLR4 signal via TIR-domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β (TRIF), which mediates type I interferon (IFN) responses.