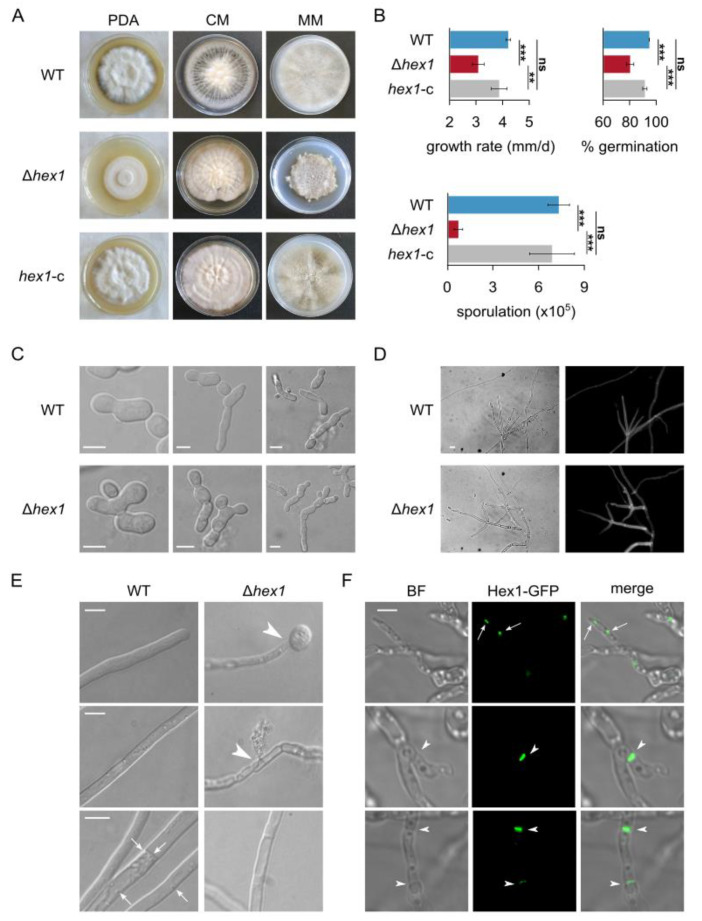
Figure 2.
Morphological and physiological characterization of the V. dahliae Δhex1 strain. (A) Colony morphologies of the V. dahliae wild-type isolate (Ls.17), the deletion mutant Δhex1, and the complemented strain hex1-c, after growth for 25 days on PDA, CzD-CM, and MM. CM: CzD-CM. (B) Growth rate, ability of conidia to germinate, and abundance of conidial production of the three strains. All experiments were performed in triplicate, and 150 conidia were tested for germination per replicate. Bars: SD. Statistical significance of differences was tested by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s post hoc test (** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, ns: nonsignificant). (C,D) Microscopic characteristics of conidia (C; bars = 5 μm) and hyphae (D; cell wall staining using calcofluor white M2R; bar = 10 μm) of the wild-type and the Δhex1 strains. (E) Response of the wild-type and the Δhex1 strains to hypotonic shock by immersing their hyphae to distilled water. Arrowheads: hyphal burst and cytoplasmic leakage. Arrows: spherical vesicles, usually localized close to the septal wall, that were observed during live-cell imaging of the wild-type strain but were absent from Δhex1. Bars = 10 μm. (F) Subcellular localization of the Hex1-sGFP tagged protein in V. dahliae. Hex1 is localized either in small globular vesicles (presumably peroxisomes or Woronin bodies (WBs), indicated by arrows) or at the septal wall (arrowheads). Bar = 5 μM.