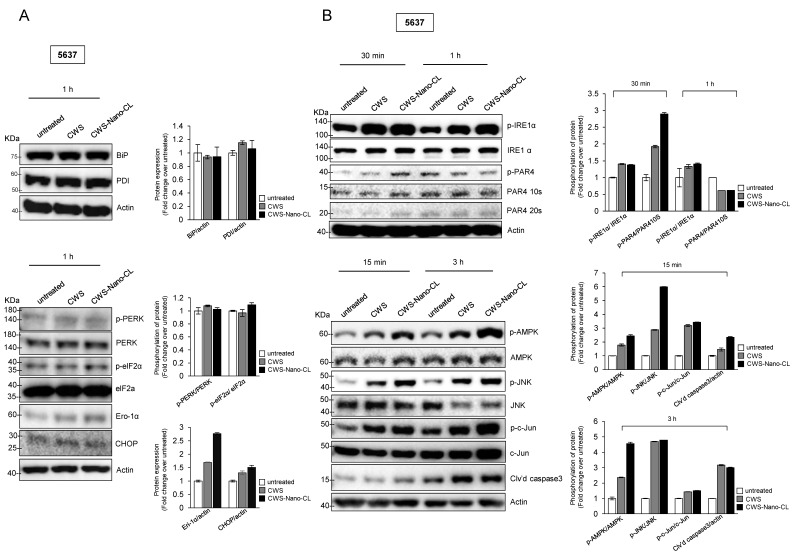
Figure 5.
Effect of CWS-loaded formulations on ER stress-induced apoptosis via AMPK activation in bladder cancer cells. (A) Cells were treated with 1 μg/mL of CWS or CWS-Nano-CL for 1 h, and then, ER stress-adaptive proteins (Bip and PDI) were detected by Western blotting (left panel). ER stress-induced mediating proteins were determined by the expression of phosphorylated PERK/PERK, phosphorylated elf2α/elf2α, Ero-1α, and CHOP (right panel). (B) Cells were treated with 1 μg/mL of CWS or CWS-Nano-CL for 30 min and 1 h, and then, phosphorylated IRE1α/IRE1α and phosphorylated PAR4/PAR4, ER stress-inducing apoptotic proteins, were detected by Western blotting (left panel). After 15 min and 3 h of treatment, the lysates were analyzed by Western blotting using specific antibodies for the indicated proteins (right panel). CWS- and CWS-Nano-CL-induced AMPK activation mediated JNK–c-Jun-caspase 3 signaling downstream of IRE1α. The blots are representative of three independent experiments. The quantification graphs represent BIP/Actin, PDI/Actin, p-PERK/PERK, p-eIF2α/eIF2α, Ero-1α/Actin, CHOP/Actin, p-IRE1α/IRE1α, p-PAR4/PAR410S, p-AMPK/AMPK, p-JNK/JNK, p-c-Jun/c-Jun, and Cl’vd PARP/Actin ratios determined by densitometric analyses. All expression ratios were normalized to the untreated group.