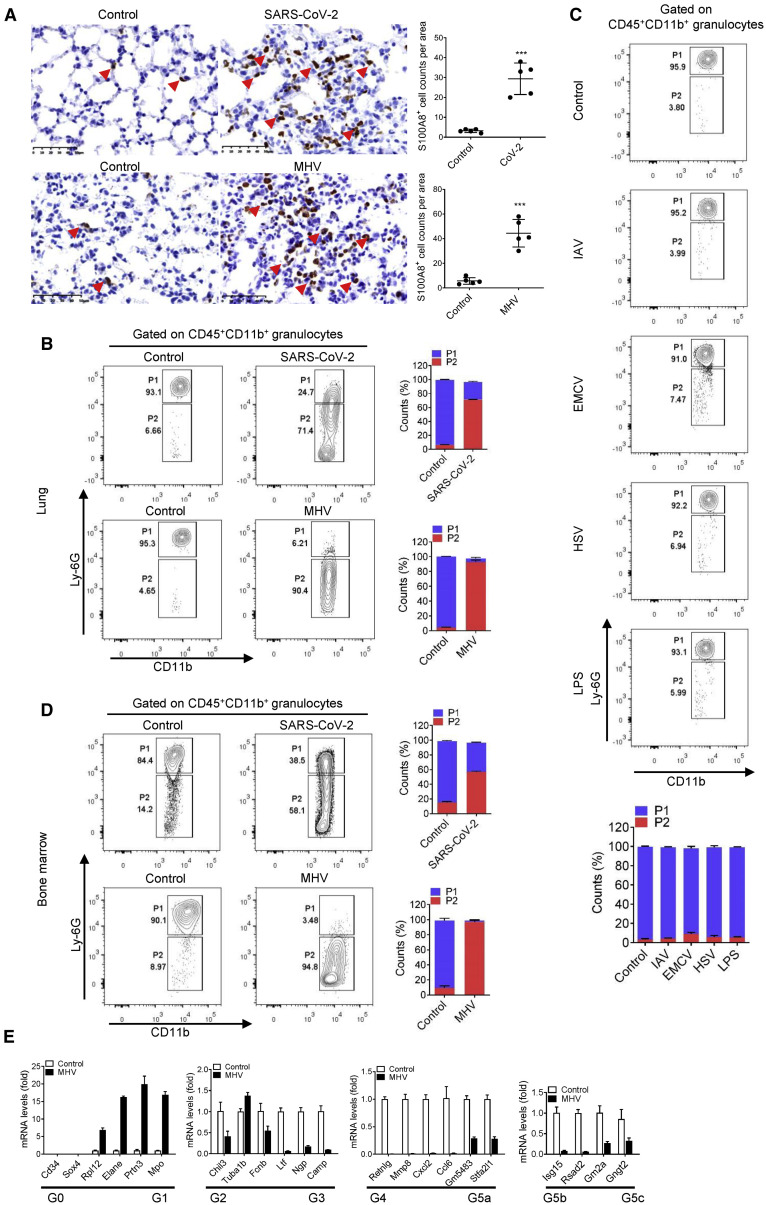
Figure 3.
A group of immature aberrant neutrophils emerged in coronavirus-infected mice
(A) Immunohistochemical analysis of the location and expression of S100A8 in the lung tissue of mice infected with SARS-CoV-2 or MHV at 5 dpi. The S100A8+ cells in the lungs of mice infected with coronavirus were increased significantly. The red arrows indicate the S100A8+ cells. n = 5. Scale bars, 50 μm.
(B) Flow cytometry analysis of neutrophils in lungs from mice infected with SARS-CoV-2 and MHV at 5 dpi. Control group means mice treated with vehicle. Gate P1 shows the conventional neutrophils (CD45+CD11b+Ly6Ghigh), and Gate P2 shows the pathologic aberrant neutrophils (CD45+CD11b+Ly6Gvariable). Aberrant neutrophils (P2) in the lungs of mice infected with coronavirus were significantly increased. n = 3.
(C) Flow cytometry analysis of neutrophils in lungs of mice challenged with IAV, EMCV, HSV-1, and LPS at 5 dpi. The results showed that these treatments did not induce an increase in aberrant neutrophils. n = 3.
(D) Flow cytometry analysis of neutrophils in bone marrow from mice infected with SARS-CoV-2 and MHV at 5 dpi. n = 3.
(E) qRT-PCR-analyzed related gene expression of aberrant neutrophils in bone marrow of mice infected with MHV at 5 dpi and identified the differentiated types of aberrant neutrophils. n = 3.
∗∗∗p < 0.001. Error bars, SD.