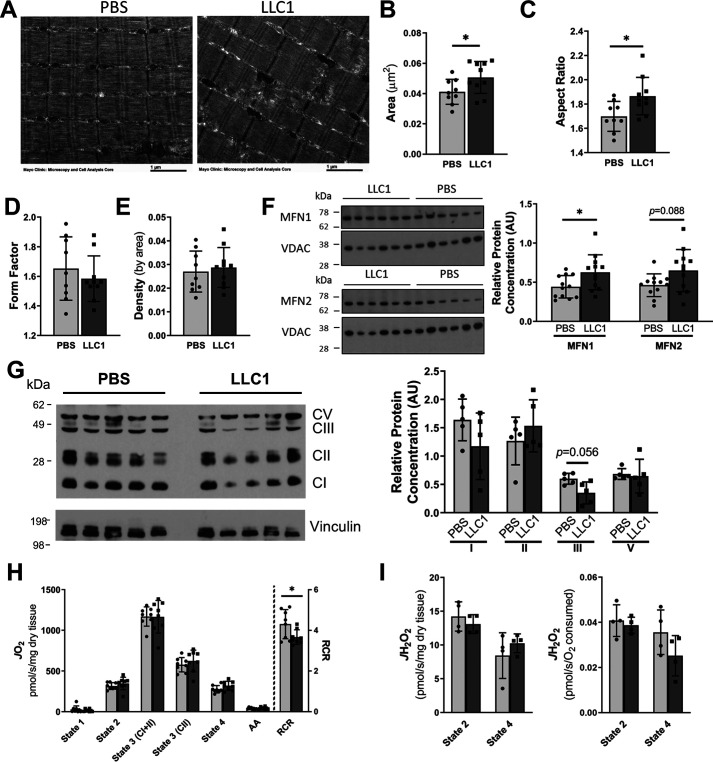
Figure 2.
Skeletal muscle mitochondrial morphology and function in tumor-bearing mice. 21 days following the injection of LLC1 tumor cells or PBS vehicle into the hind-limb of 7-week–old mice, the mitochondrial morphology and function of skeletal muscle was assessed. A–E, transmission EM images of gastrocnemius muscle were used to assess mitochondrial morphology, including mitochondrial; B, cross-sectional area; C, aspect ratio; D, form factor; and E, density by area. F, protein expression of the mitochondrial fusion proteins mitofusin (MFN) 1 and MFN2 in gastrocnemius tissue were assessed by Western blotting and normalized to voltage-dependent anion channel protein concentration. G, the simultaneous assessment of the protein levels of the electron transport chain complexes in the gastrocnemius was assessed by Western blotting. Protein expression was normalized to vinculin concentration. H and I, simultaneous high resolution respirometry and fluorometric measurement of H2O2 was used to assess (H) respiration and (I) ROS production in permeabilized extensor digitorum longus muscles. Light bars represent PBS-injected mice and dark bars represent LLC1-injected mice. *, represents significant difference (p < 0.05) between LLC1- and PBS-injected mice. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. MFN, mitofusin; CI–CV, complex I–complex V; AA, antimycin A.