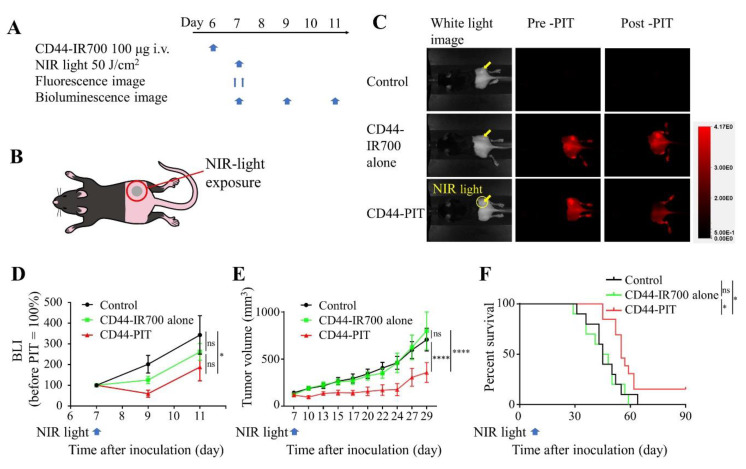
Figure 3.
CD44-targeted NIR-PIT treated MOC2-luc tumors with limited success. CD44-targeted NIR-PIT was tested on MOC2-luc tumor-bearing mice. Control, no treatment; CD44-IR700 alone, i.v. injection of anti-CD44-IR700 only; CD44-PIT, i.v. injection of anti-CD44-IR700 with NIR light exposure. (A) NIR-PIT regimen. Bioluminescence and fluorescence images were obtained at each time point as indicated. (B) Laser-light exposure. NIR light was administered on the tumor only. (C) In vivo IR700 fluorescence imaging of tumor-bearing mice before and after the NIR-PIT. The yellow arrows indicate the tumor locations. (D) In vivo BLI of tumor-bearing mice before and after NIR-PIT. Luciferase activity was quantified and shown in relative percentage to the signal intensity before treatment in three treatment groups (n = 10–13; *, p < 0.05; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). (E) Tumor growth curves (n = 10–13; ****, p < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). (F) Kaplan–Meier survival analysis following NIR-PIT treatment (n = 10–13; *, p < 0.05; log-rank test followed by Bonferroni correction). Each value in D and E represents means ± SEM of independent experiments.