Fig. 2.
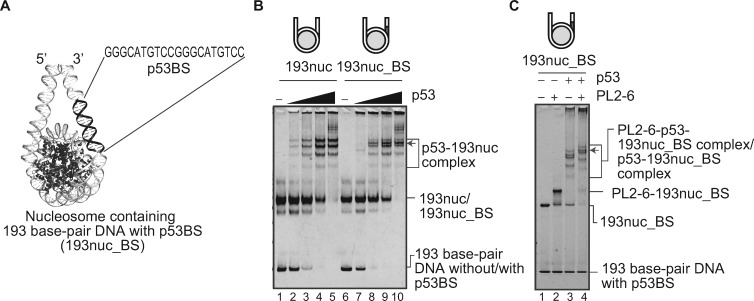
The p53 target sequence induces specific p53-nucleosme complex formation. (A) The structural representation of the predicted p53 target sequence (p53BS) location in the nucleosome containing the 193 bp DNA (193nuc_BS) (modified from PDB ID: 5NL0). (B) EMSA for p53 binding to nucleosomes with or without p53BS. Increasing amounts (0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8 µM) of p53 were mixed with 193nuc (lanes 1–5) or 193nuc_BS (lanes 6–10). The nucleosome concentration was 0.1 µM. p53 binding was detected by non-denaturing PAGE, followed by ethidium bromide staining. The additional band is indicated by an arrow. The reproducibility was confirmed by repeated experiments. (C) EMSA for p53-nucleosome complex binding to the PL2-6 antibody. p53 (0.8 µM) and 193nuc_BS (0.1 µM) were mixed, and then the PL2-6 antibody (0.3 µM) was added. The samples were analysed by EMSA with a 5–12% gradient gel, followed by ethidium bromide staining. The reproducibility was confirmed by repeated experiments. The shifted additional band is indicated by an arrow.