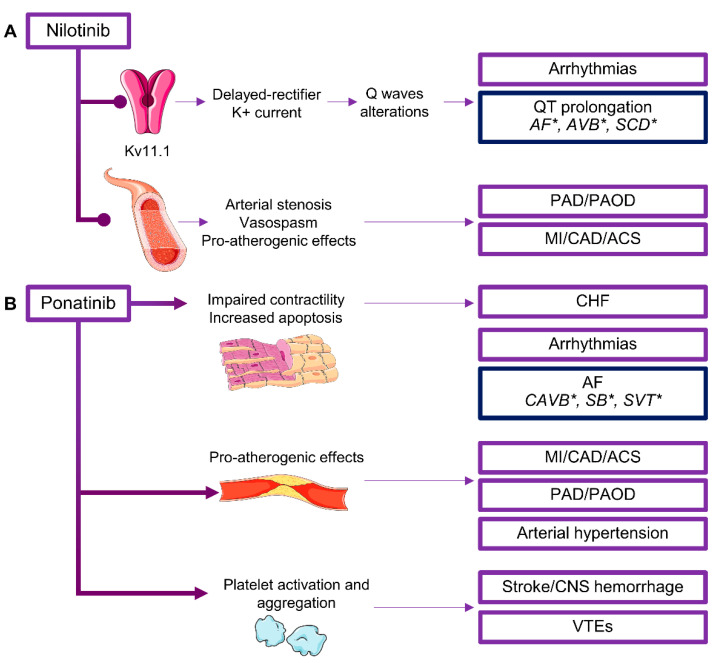
Figure 3.
Cardiotoxicity of B cell receptor (BCR)/ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). Cardiotoxicity of (A) nilotinib and (B) ponatinib. Inhibitors of BCR/ABL activity cause various forms of cardiotoxicity, such as congestive heart failure (CHF), myocardial infarction (MI), acute coronary syndrome (ACS), coronary artery disease (CAD), peripheral artery disease (PAD), peripheral arterial occlusive disease (PAOD), venous thromboembolisms (VTEs), and arrhythmias. SCD, sudden cardiac death; SVT, supraventricular tachycardia; CAVB, complete atrioventricular block; SB, sinus bradycardia. * Uncommon and rare cardiotoxicity (frequency <1% or case reports).