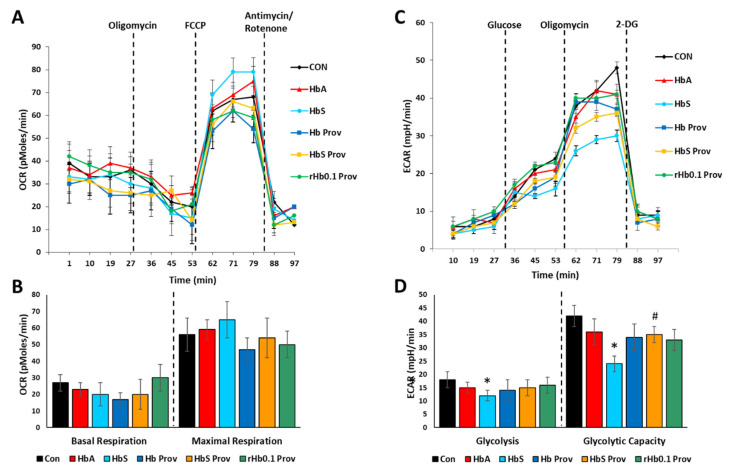
Figure 5.
Effect of mutant hemoglobin proteins on pulmonary endothelial bioenergetics. HPAECs were exposed to ferrous forms of HbA, Providence (βK82D), HbS, HbS Providence (βE6V/βK82D), or crosslinked Providence (rHb0.1/βK82D) at an equimolar concentration (100 µM) for 24 h. Mitochondrial oxygen consumption rates (OCR) and extracellular acidification rates (ECAR) were measured by Agilent Seahorse (XF24) extracellular flux analyzer in real time. (A) Bioenergetic profile indicating average OCR values from four similar wells treated with Hb mutants. (B) Bar diagrams showing basal and maximal respiration (OCR) calculated from the OCR plots (A), following exposure to Hb (N = 4). (C) Glycolytic lactate production was measured as ECAR and plotted as the average of four similar wells treated with Hb mutants. (D) Basal glycolysis rate and glycolytic capacity were calculated from the ECAR plots of HPAEC, following exposure to Hb (N = 4). Representative OCR and ECAR plots were obtained from an individual set of experiment repeated three times. * p < 0.05 vs. the untreated control; # p < 0.05 vs. corresponding HbS.