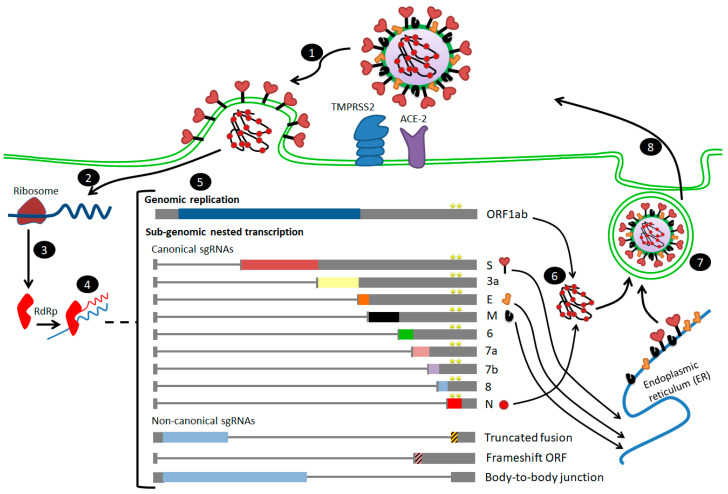
Figure 2.
Steps of SARS-CoV-2 infection and entry to the host cell [14,29]. (1) After receptor (angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)) binding, the virus enters host cell cytosol via cleavage of S protein by a protease enzyme (transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2)), followed by fusion of the viral and cellular membranes. (2) Upon cell entry, the genomic RNA is translated to produce non-structural proteins from two open reading frames, ORF1a and ORF1b. (3) Some of the nsps have RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) activity (nsp12). (4) Negative-sense RNA intermediates are generated to serve as the templates for the synthesis of positive-sense genomic RNA (gRNA), and (5) sub-genomic RNAs (sgRNAs). (6) The gRNA is packaged by the structural proteins to assemble progeny virions. Shorter sgRNAs encode conserved structural proteins (S, E, M and N), and several accessory proteins. SARS-CoV-2 is known to have at least six accessory proteins (3a, 6, 7a, 7b, 8 and 10), and non-canonical sgRNAs are also shown in the figure. The AAGAA-type modification clusters in gRNA and sgRNAs are shown with yellow stars annotations. (7,8) budding and exocytosis of the virus occur.